|
|
|
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
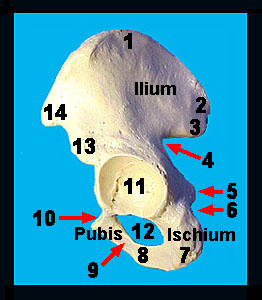
This image shows a medial view of the coxa (also called the innominate bone). Note the prominent iliac crest that runs anteriorly from the tuberosity to terminate in the anterior superior iliac spine. The anterior inferior iliac spine is located immediately below the anterior superior iliac spine. The ilium contributes approximately one-third to the upper portion of the acetabulum. The acetabulum is a deep socket on the lateral surface of the coxal bone where the femur articulates. The body of the pubic bone is also a component of the acetabulum and it gives off an anterior process termed the superior ramus. Anteriorly the superior ramus expands to form the pubic crest. The pubic crests from each coxal bone join anteriorly to form the pubic symphysis. An inferior ramus of the pubis comes off the pubic crest and fuses with the ischial ramus of the ischium. The body of the ischium forms the remaining one-third of the acetabulum and sends off an inferior process - the ischial ramus (mentioned above). This ramus articulates with the inferior ramus of the pubis. Roughened projections of the ischium called ischial tuberosities form the posterior-lateral borders of the bone; these projection bear the weight of the body when seated. Also note the ischial spine that projects medially from the ischium. Inferior to the ischial spines is the lesser sciatic notch through which a number of nerves and blood vessels pass to and from the pelvis and thigh. |
|