|
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
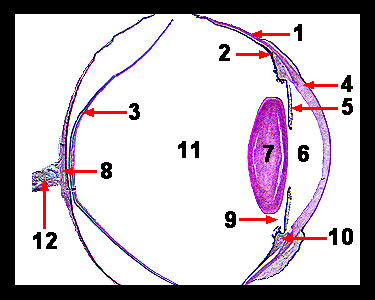
This slide shows a section of a monkey eye. On the anterior surface of the eye is the transparent cornea, which is continuous with the sclera, a tough, white outer coat of the eyeball that helps maintain the spherical shape of the eyeball. The middle layer of the eye wall is the vascular tunic, the posterior portion of which is called the choroid. The choroid contains many blood vessels and dark pigments that absorb stray light. The anterior portion of the choroid becomes the ciliary body to which the lens attaches. This structure contains a type of smooth muscle called ciliary muscle. The most anterior portion of the vascular tunic is the iris (the colored portion of the eye), which has a hole in the center called the pupil. The iris contains smooth muscle fibers that can change the diameter of the pupil, thus regulating the amount of light which enters through it. The retina (the sensory portion of the eye) is normally attached to the eyeball at one spot opposite the lens that is called the blind spot, but on this slide, the retina has become detached in preparation. The lens is a transparent structure and performs the final fine focusing of light rays. The thickness of the lens can be adjusted by changing the tension on its attachments (suspensory ligaments) to a structure called the ciliary body, which possesses the ciliary muscles and small extensions called ciliary processes. The space just behind the cornea is the anterior chamber. The space between the iris and the lens is the posterior chamber. The anterior and posterior chambers are filled with a fluid called the aqueous humor. The space behind the lens is called the vitreous chamber or posterior segment, which is filled with a gelatinous material called the vitreous humor. |
|