|
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
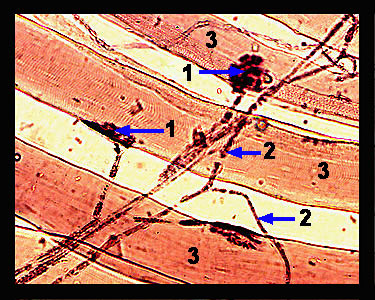
This image shows a longitudinal view of several skeletal muscle fibers along with the terminal branches of the motor (efferent) nerve that innervates them. Note the specialized portions of the sarcolemma (muscle cell membrane) called motor end plates. Although the ends of axons come close to the muscle fibers, they do not actually touch, and it is a chemical signal that bridges the gap between the axon terminal and the motor end plate. This neurotransmitter chemical (acetylcholine) is released from presynaptic vesicles when the nerve impulse reaches the end of the axon. Special receptors on the sarcolemma respond to acetylcholine by initiating a depolarization of the muscle cell, which causes it to contract. |
|