|
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
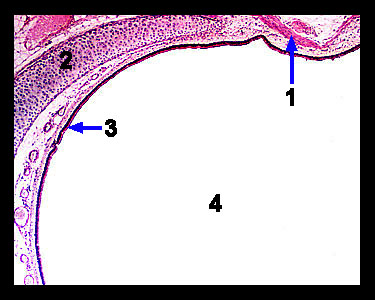
This image shows a cross section from the trachea. Note that the lumen of this organ is lined with ciliated pseudostratified columnar epithelium. Interspersed among these cells are mucus-secreting goblet cells. The cilia move the mucus layer loaded with dust particles, bacteria, and other debris toward the pharynx where it can either be swallowed or expectorated. Seromucous glands located in the submucosa just beneath the ciliated pseudostratified columnar epithelium produce additional airway secretions. The wall of the trachea contains C-shaped rings of hyaline cartilage. The open ends of the cartilage rings are located posteriorly and lie against the esophagus. These C-shaped rings of cartilage support the trachea and prevent it from collapsing during the breathing cycle. The open portions of the rings are connected by smooth muscle cells that form the trachealis muscle. This soft tissue permits the esophagus to expand anteriorly during swallowing. |
|