|
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
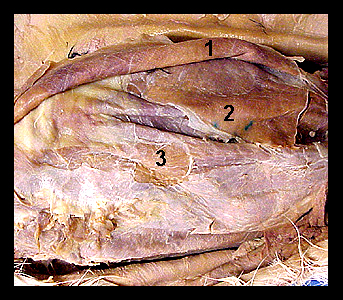
This image shows a ventral view of the abdominal wall of a cat, with the external oblique muscle reflected laterally. The external oblique forms the most superficial of the three layers of abdominal muscles. The internal oblique lies directly beneath the external oblique. Its fibers extend caudodorsally, nearly at right angles to the fibers of the external oblique. The rectus abdominis lies between the aponeuroses of the internal oblique and the transversus abdominis for most of its length. |
|