|
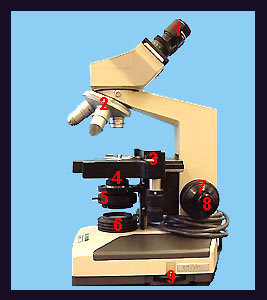
The compound microscope is one of the most important and useful tools for the biological and health sciences. Before actually using the microscope, you should familiarize yourself with its principal parts and controls. At the top of the microscope are the two eyepieces (ocular lenses) that are inserted into inclined body tubes. Below the eyepieces is the arm which is attached to the base. Above the base is the stage, which is equipped with a mechanical stage that holds the slide and allows it to be positioned with two adjustment knobs. Above the stage is the rotating nosepiece, which holds four objective lenses. Below the stage is the substage condenser, which serves to focus the light rays from a quartz-halogen illuminator onto the specimen. The intensity of this light source is adjusted with a rheostat located on the side of the base. Below the condenser is an iris diaphragm that can be adjusted with a protruding lever. On the side of the arm near the base are the coarse and fine adjustment knobs, which are used to focus the specimen. Total Magnification is computed as the product of the magnifications of the eyepieces and objective lens. As the objective power increases, so does its length as well as the risk that it can be damaged by misuse or that it can damage a slide. As total magnification increases, field of view (how much of the specimen you can see), depth of field (how much of a vertical area remains in focus) and light intensity decrease. Therefore, when switching from one objective to another, you will probably have to make adjustments with the light intensity switch, iris diaphragm and substage condenser to ensure that the specimen continues to be viewed under the best conditions. |
|