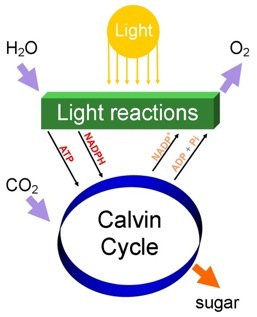
Like all plants, Toxicodendron radicans are primary producers that generated their own food. With the components carbon dioxide, water, and sun light a plant is able to create sugar, oxygen, and water. The sugar, in the form of sucrose is the plants energy source. The oxygen is essential in respiration for organisms such as ourselves.
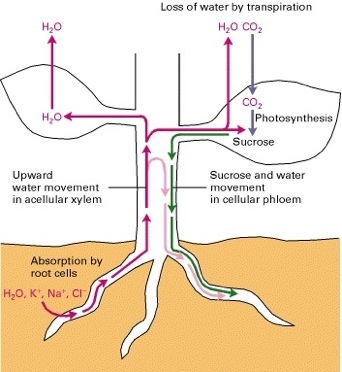
Photosynthesis occurs in the chlorophyll of the leaves. So how does water from the ground get up to the leaves and how does the sucrose in the leaves able to supplement the whole plant? The simple answer is vascular tissue! The vascular tissue responsible for the transportation of water is xylem and the vascular tissue responsible for the transportation of sucrose and other nutrients is ploem.