The active ingredient of poison ivy that causes an allergic reaction in humans is Urushiol. Urushiol is an oil in the sap of the plant. Sap runs through all parts of the plant, so a person can get the negative effects from touching not only the leaves, but also the stem and roots. However, just because you were not exposed to the plant does not mean you are safe from the rash. Urushiol is remains potent on items that have been in contact with the plant. For example if you pulled out a poison ivy plant from your garden wearing gloves and then two months later touched the outside of the gloves there is a good chance you will have the allergic reaction. The urushiol binds with the proteins in the fatty cells beneath the epidermis.


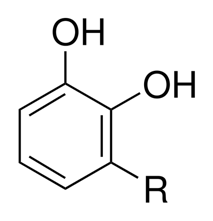
Contact with poison ivy is one of the most reported cases at poison centers in the United States. The clinical name for the allergic reaction is Rhus Dermatits and the caliber of the reaction depends how sensitive a person is to it and the intensity of the exposure. Some people are immune to it and some are immune and become sensitive to it later in life.
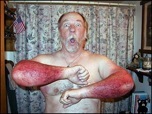
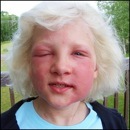
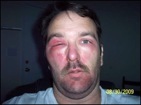
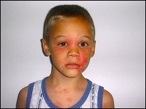
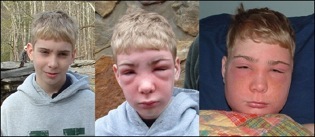
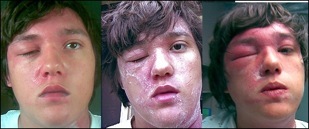
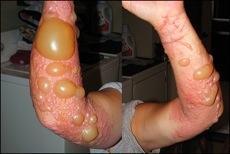
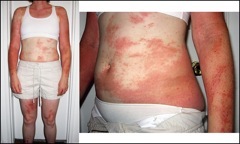
The first sign of being exposed is a small, itchy rash after about 12 hours. The rash may stay just an extremely itchy spot but in most cases will swell and develop blisters. The rash lasts usually between 1-3 weeks depending on the severity and how it is treated. There are prescription medications that aid in the process.
Take a look at the types of rashes poison ivy can cause!
Urushiol