Classification: Giant Among Raptors
Harpia harpyja (Linnaeus, 1758)
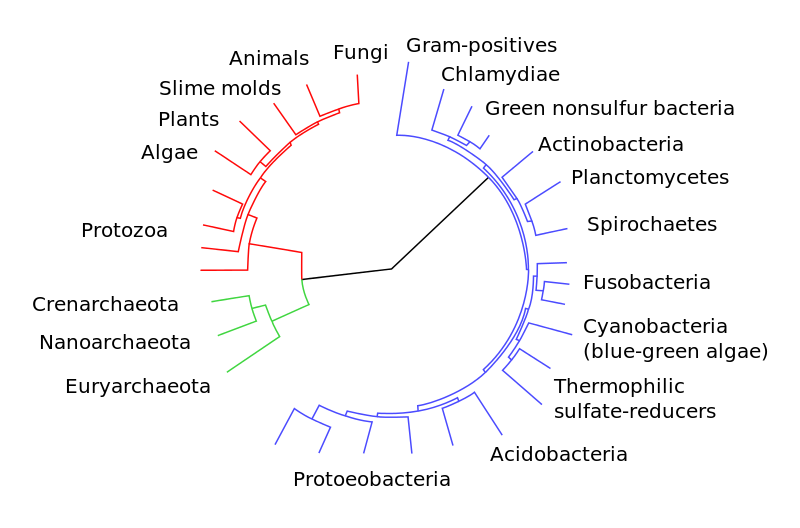
Domain: Eukarya
Any organism with a true
nucleus and cell membrane bound organelles falls into the domain of
Eukarya. This domain contains animals, fungi, plants, and protists.
The phylogeny tree above indicates the vast variety of organisms,
including Eukarya. The Harpy Eagle would fall under the animal node.
To see a variety of different species from this domain and others,
please visit the Multiple
Organisms website where you will find things like
Mangrove Tunicates,
Jelly Ear
Mushrooms, and the
Giant
Pacific Octopus!
Kingdom: Animalia
To be considered part of the kingdom
Animalia the organisms must be heterotrophic, or consume their food
instead of producing it. Other characteristics present in the
Animilia kingdom are multicellularity, mobility, and a lack of a
structural cell wall.
The kingdom
Animalia encompasses so many organisms, here are a few more:
Damselfly,
Mute
Swan, and
The North
American Beaver
Phylum: Chordata
Chordates are deuterostomes, which means the
anus develops before the mouth. To be a member of the phyla chordata
a dorsal hallow nerve chord must be present; there must also be a
tail extruding beyond the anus and pharyngeal gill slits.
Other chordates include:
Yellow Perch,
Timber
Rattlesnake, and the
Green Frog
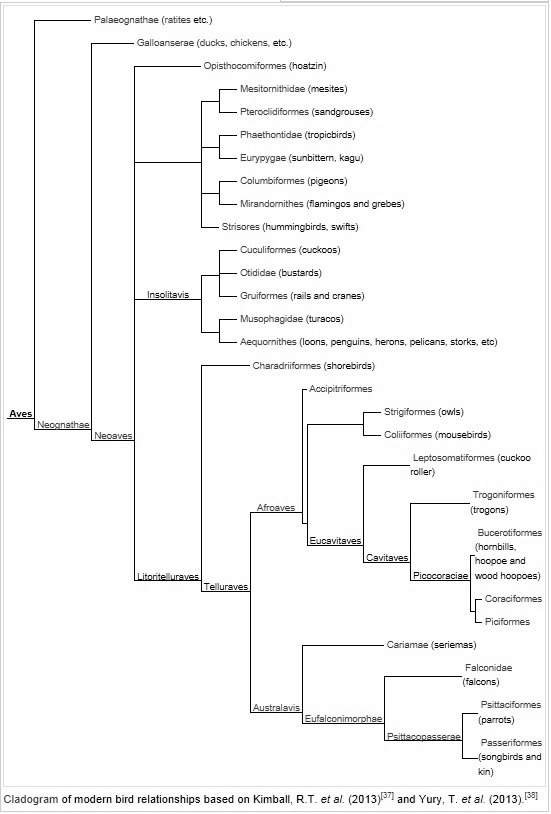
Class: Aves
Aves, more commonly known as birds, have a very
unique set of characteristics which evolutionarily helped with the
ability to fly. To highlight a few, Aves are warm blooded, have
lightweight or hollow bones, and feathers.
Below is a phylogenic tree of the Aves class. Even within this group
there is still a lot of diversity. The Harpy Eagle would be located
near the bottom of the tree, under the Falcons tip, which would
continue to break down into more closly related organisms.
If the Aves Class interests you, here are a few more interesting
organisms: The
Green Heron,
American
White Pelican, or the
Barred Owl
Order: Falconiformes
Falconiformes are diurnal birds, meaning
they sleep at night and maintain activity such as hunting during the
day.
Family: Accipitridae
Eagles and other members of the Accipitridae
family are carnivorous birds. Evolution favored powerful wings for
long distance flight and powerful claws for capturing and devouring
prey.
A closley related organism to the Harpy Eagle that shares its same
family is the
Red-tailed Hawk, check it out!
Genus: Harpia
Harpy Eagles have the largest body and talon size
of all species of eagles.
Species: Harpia harpyja
Also referred
to as the American Harpy Eagle, can commonly be found in tropical
South America. Their feather pattern presents itself in varying
shades of grey and black with very distinct feathers on the back of
its head. Harpy Eagles primarily consume small to medium sized mammals like
sloths or monkeys.