Top Secret!!!
Classified Information
| *Scientific Name: Cyathus striatus *Common Name: Bird’s Nest Fungi *The Complete Classification of the Organism: |
 |
Cyathus striatus fits into the Eukarya domain because it is eukaryotic and therefore has a membrane bound nucleus and other specialized organelles in the cytoplasm (Ulloa, March 12, 2007).
-Kingdom: Fungi
Cyathus striatus fits into the kingdom of fungi because it is multicellular, has cell walls composed of chitin, and is non-vascular. Also, this fungus lives by decomposing and absorbing the organic material in tree bark or wood mulch (Hine, March 12, 2007).
-Phylum: Basidiomycota
Cyathus striatus is part of the phylum Basidiomycota because it reproduces
sexually by producing basidiospores inside the basidia (Magill, March 12, 2007).
-Class: Gasteromycetes
Cyathus striatus is part of the class Gasteromycetes, a division of fungi that
includes species where the hymenium is enclosed until the spores have matured.
The hymenium is the spore bearing layer of the fruiting body and contains basidia (Volk, March 12, 2007).
-Order: Agaricales
Cyathus striatus belongs to the order Agaricales, because it is a fungus that has
gill-like structures. Also, members of Agaricales are commonly known for their
peridioles being ejected or splashed out of their nest (Volk, March 12, 2007).
-Family: Nidulariaceae
Cyathus striatus belongs to the family Nidulariaceae, because commonly within this family the fruiting bodies of fungi are about 15 mm high and 10 mm wide. Also, one of the main shapes of fungi from this family is cup or vase shaped. In addition, all the fruiting bodies within the family, Nidulariaceae, contain peridioles (Miller, March 12, 2007).
-Genus: Cyathus
Cyathus striatus fits into the genus Cyathus because it is a major subdivision of the Nidulariaceae family. Also, this fungus is classified under Cyathus because the
peridioles are dark in color. Furthermore, most species of Cyathus use non-living
organic matter as the substrate they invade (Margulis, March 12, 2007).
-Species: Cyathus striatus
This fungus fits into the species, Cyathus striatus, because it is a major
subdivision of the genus Cyathus. Also, this fungus fits into this species because the origin of the name "striat" refers to the interior of a splash cup being striated (Miller, March 12, 2007).
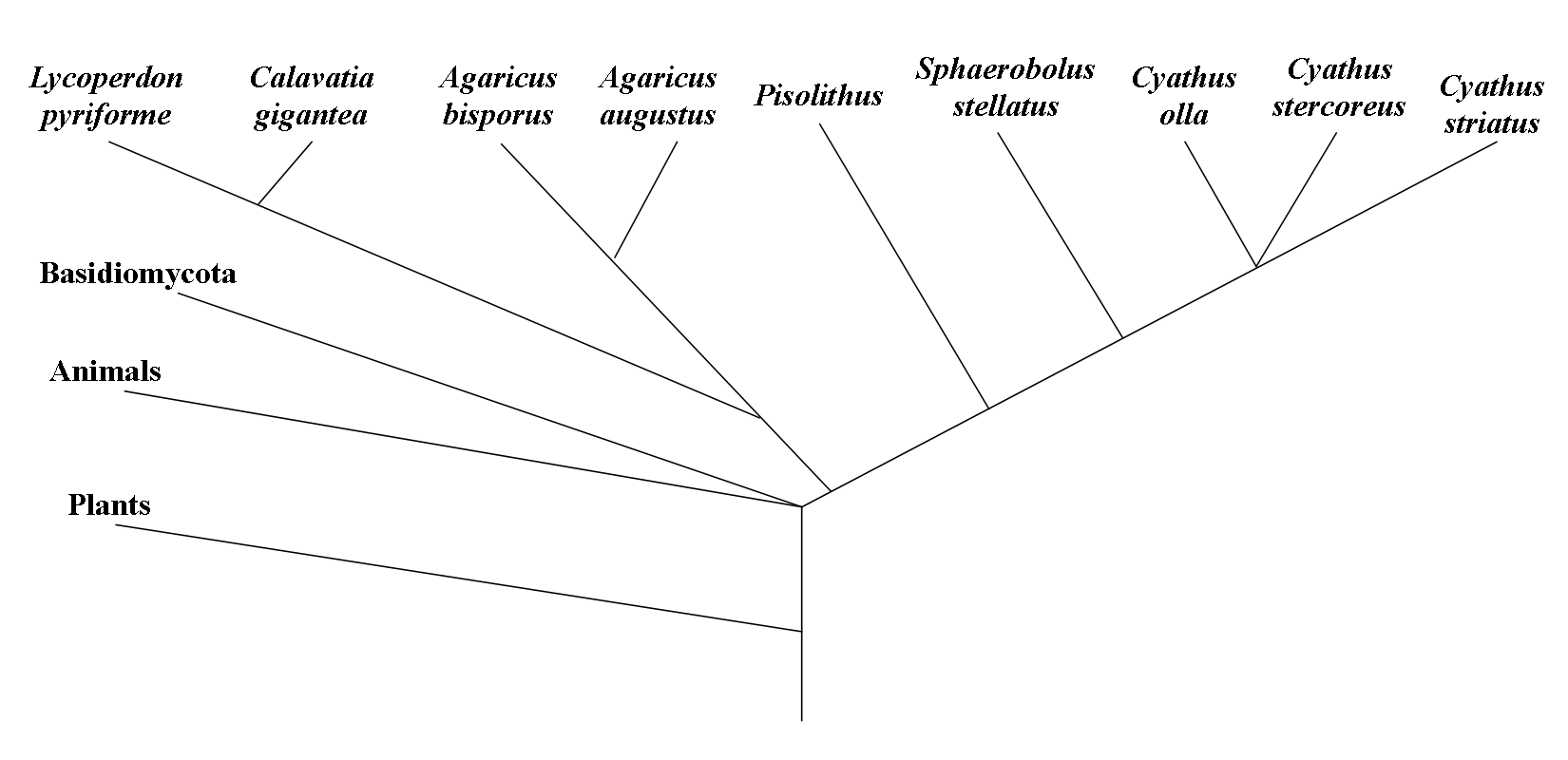
The information necessary to create this phylogenetic tree was gathered from Tom Volk, David S. Hibbett, and Elizabeth M. Pine.
For more information on the nutrition and adaptations of Cyathus striatus click here.