|
Acinonyx jubatus
Domain-Eukarya
Kingdom-Animalia
Phylum-Chordata
Class-Mammalia
Order-Carnivora
Family-Felidae
-
Cat
family, rounded heads with short muzzles, strong teeth, five toes/claws on
front limbs and four on back limbs.
Genus-Acinonyx
-
Cat is
not a good climber and relies on speed rather
than stealth to catch prey.
In greek Acinonyx means
"no-moved claw." (Old world cheetah)-long-legged, spotted cat, non retractile claws. Present-day
cheetah actually has
semi-retractile claws.
Species-jubatus
Subspecies due to
habitat location:
South Africa- A.j.
jubatus East Africa- A.j. velox
East Africa- A.j.
raineyi Sudan- A.j. soemmeringii
North Africa-A.j.
hecki
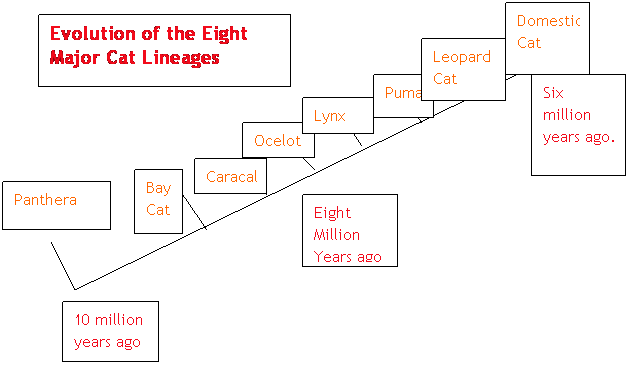
This phylogenetic
tree shows the evolution of the
eight major cat lineages. However, the
actual evolution
of today's cats did not occur in this order. This tree
shows that some cats evolved independently from each other. For
example,
cheetahs evolved about 5.5 million
years ago and are part of the Puma lineage.
Present day lions, tigers,
and jaguars evolved about 1.6 million years
ago.
These cats are part of the panthera lineage. The
closest living relatives
to the cheetah are pumas.
Send Comments about this page to
David Marek
|
