|











| |
Habitat:
Bald eagles are found for the most part
exclusively in the North America continent, but some are known to stray to
Siberia and Greenland on occasions. Although they are found over the whole
continent, breeding is most prevalent in Alaska, Florida, the Pacific Northwest,
the great lake states, and the Chesapeake Bay region.
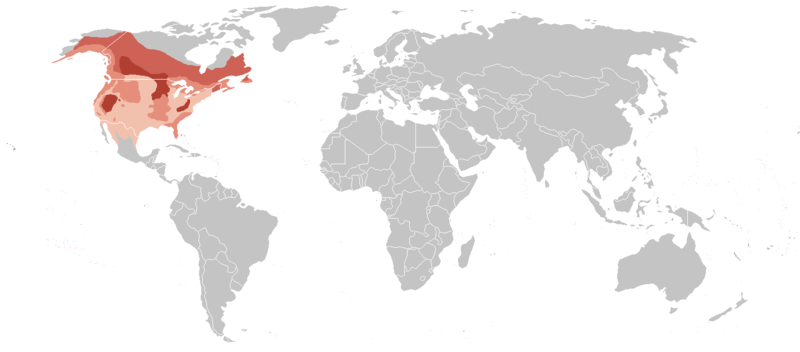 |
Bald Eagle Distribution
-
██ Winter
-
██ Year-round
-
██ Breeding
-
██ Migrant
|
Bald Eagles are not generally viewed as migratory birds, but have been known
to do so when food supply has dwindled. This is the case in many of the northern
regions that eagles reside because when the lakes and streams freeze over,
fishing is impossible and the other sources of food (mainly other birds) migrate
south.
Bald eagles use their habitats for different purposes:
- Nesting
- Perching
- Roosting
- Foraging
 |
Nesting - Bald eagle nests are always located near bodies of water,
most often lakes and seas but on rare occasions a nest can be found around a
river. The eagle is very specific on the type of tree that it selects for its
nest, and will sacrifice the close proximity to water if no quality trees are
available. The tree is usually one of the tallest in the forest in order to
provide an adequate support for the large nest, and it offers a 360 degree
panoramic view of the surrounding area. Another possible reason for the tall
tree being selected is to provide for unobstructed flight to and from the nest.
This is important because bald eagles are large birds and have difficulty
maneuvering in densely wooded areas. |
Perching - The vast majority of the bald eagle's time during
the day is spend perching; some estimates suggest up to 90% of daylight
hours. The trees selected for perching do not have to pass the rigorous
guidelines as the nesting trees, but are still located along shorelines.
The purpose of perching varies, but they can act as:
- An observation post while hunting
- A spot to feed on the prey they recently caught
- A guard post to watch over offspring or for possible predators
- A spot to display messages, usually to other eagles, about the
availability or location of food and mating calls.
- A spot to bask in the sun to help thermoregulate.
- A spot to rest.
|
 |
 |
Roosting - The location where eagles sleep or rest during the night,
which does not need to be close to water. Foraging - Requires large open areas where prey is very abundant.
Foraging areas cover a very large area of land and sometimes are communal. Bald
eagles do not restrict themselves to one foraging area, and often move from one
to another freely based on the availability of food.
|
|
The Alaska
Peninsula National Wild Life Reserve offers an example of a foraging
area. |
|
|




