|
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
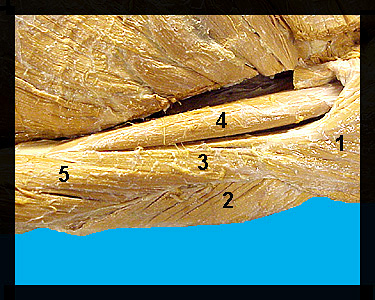
This image shows several of the muscles on the arm of a male human cadaver. As previously mentioned, the deltoid abducts the arm and aids in flexion and extension. The triceps brachii (which consists of three heads) functions to extend the forearm. The brachialis originates on the humerus and inserts on the ulna; its action is to flex the forearm. The brachialis is located on the anterolateral surface of the humerus and is partially covered by the lateral head of the triceps brachii. It originates on the humerus and inserts on the ulna. The brachialis functions to flex the forearm. The biceps brachii (which has two heads) produces flexion of the forearm and supination of the hand. The brachioradialis is a narrow band-like muscle that passes along the medial border of the forearm. Its origin is the humerus where the brachioradialis appears to be continuous with the brachialis. The major action of the human brachioradialis is flexion of the forearm. |
|