|
|
|
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
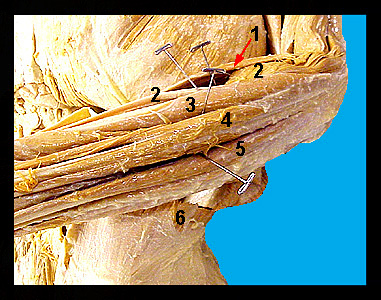
This image shows some of the muscles of the forearm of a human cadaver. The brachioradialis is a narrow band-like muscle that passes along the medial border of the forearm. Its origin is the humerus where the brachioradialis appears to be continuous with the brachialis. The major action of the human brachioradialis is flexion of the forearm. The extensor carpi radialis longus and extensor carpi radialis brevis are located beneath the brachioradialis. Their origin is the lateral surface of the humerus above the lateral epicondyle and their insertion is on the metacarpals. Note that the extensor carpi radialis brevis is the shorter of the two. These muscles extend and abduct the wrist in humans. As the name implies, the extensor digitorum extends the wrist and digits. The extensor carpi ulnaris originates from the lateral epicondyle of the humerus and inserts on the lateral aspect of the fifth metacarpal. This muscle extends and adducts the wrist. As mentioned previously, the external oblique (along with other abdominal muscles) serves to compress the abdomen. |
|