Classification
Domain: Eukarya
Kingdom: Animalia
Phylum: Chordata
Class: Mammalia
Order: Carnivora
Family: Canidae
Genus: Vulpes
Species: vulpes
Domain: Eukarya- Organisms in the Domain Eukarya possess membrane bound organelles (Myers, 2001).
Kingdom: Animalia (Animals)- Members of this class obtain energy from other organisms because they are unable to produce it themselves (Myers, 2001).
Phylum: Chordata (Possess a basic 'backbone')- Members of the Phylum Chordata have bilateral symmetry. They are highly cephalized, meaning they have a concentration of sensory organs. Members are triploblastic, denoting three tissue layers, and possess a coelom. They also have have a complete digestive tract and notochord. Additionally, they also have a post anal tail present during some point of their life cycle (Myers, 2001).
Class: Mammalia (Mammals)- All organisms of this class Mammalia have bodies covered in hair. They are endothermic and nourish their young with milk. Embryos develop internally in members of this class (Myers, 2001).
Order: Carnivora (Possess carnassial teeth)- Members of this order are carnivorous, or meat eating. They may have other dietary habitats as well (Myers, 2001).
Family: Canidae (Dogs)- This family includes coyotes, dogs, foxes, jackals, and wolves. Usually have five toes on the fore feet and have four toes on the hind feet. They have non retractable claws (Myers, 2001).
Genus: Vulpes (from Latin meaning 'fox')-Members
referred to as true foxes. They have black triangular markings
between the eyes and nose, and the tips of their tales are often a
different color from their pelts (Myers, 2001).
Species: Vulpes vulpes-Most widely distributed carnivore in the world (Myers, 2001).
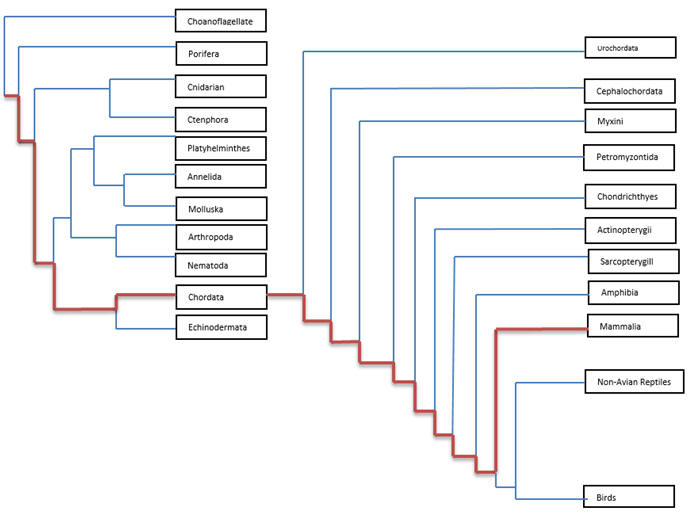 Figure 1.
Phylogenetic tree created by Emilee DeSmet showing the relationship
of the phylum Chordata and class Mammalia.
Figure 1.
Phylogenetic tree created by Emilee DeSmet showing the relationship
of the phylum Chordata and class Mammalia.
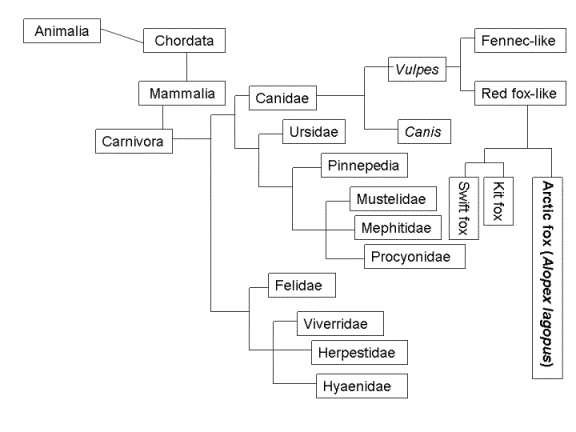
Figure 2. This is a phylogenetic tree showing the relationship of the red fox to the animalia kingdom.
To learn about where the red fox lives, visit the habitat page!