Habitat
The Mexican Red Rump Tarantula is indigenous to Central
America. However due to the domestication of the tarantula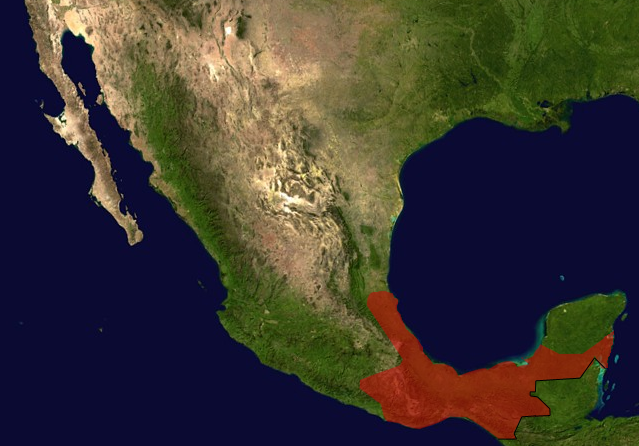 as a
exotic pet this spider has been found wild in parts of Florida
as well (Machkour et al. 2011 2). The spider thrives in warm
tropical climates found in these countries. The Mexican red rump
spider inhabits many places in Latin American rural
villages (Machkour et al. 2011 2). This can cause serious problems
for the spider population despite the fact that Mexican red rump
tarantula is not harmful to humans.
as a
exotic pet this spider has been found wild in parts of Florida
as well (Machkour et al. 2011 2). The spider thrives in warm
tropical climates found in these countries. The Mexican red rump
spider inhabits many places in Latin American rural
villages (Machkour et al. 2011 2). This can cause serious problems
for the spider population despite the fact that Mexican red rump
tarantula is not harmful to humans.
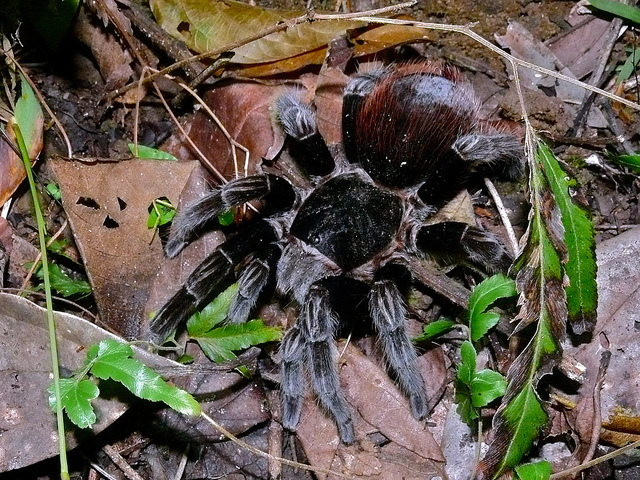
Mexican red rump spiders are a threatened species (Machkour et
al. 2011 1). The spiders are suffering from a specific type of
habitat destruction in their native areas. The type of
destruction is referred to as habitat isolation by Machkour and
Henaut. What happens is a population of the spiders inhabits a
certain area but then due to outside influences the population
gets separated by an outside force this force acts as a wall
breaking the population into smaller populations of spiders.
Some of these Forces include agriculture, roads and this means
that population so spiders is smaller thus limiting genetic
diversity. This makes all the sub populations more susceptible
to potentially deadly influences and can wipe out spider
populations. Also with small populations of B. vagans
reproduction can cause difficulties this is due to their very
aggressive nature. Mexican red rumps have been known to burrow
in a close vicinity which often leads to confrontations and
fights between tarantulas.
 The main area that this is happening in is the Caribbean side of
Latin America. Due to massive sugar cane plantations (Machkour
et al. 2011 1). Because the tarantula is a burrowing spider it
cannot create its burrows on plantation areas with plowing and
cultivating of the land. This separates the population of
tarantulas geographically, causing the formation of new smaller
sub populations. The reason these small populations lack in
genetic diversity is they don’t have enough individuals to
create a substantial amount of genetic variation (Machkour et
al. 2011 1). This coupled with the Brachypelma vagans aggressive
and cannibalistic nature cause even less genetic variation. This
leads to a great amount of inbreeding which can weaken the
population and make it more susceptible to disease and other
environmental influences.
The main area that this is happening in is the Caribbean side of
Latin America. Due to massive sugar cane plantations (Machkour
et al. 2011 1). Because the tarantula is a burrowing spider it
cannot create its burrows on plantation areas with plowing and
cultivating of the land. This separates the population of
tarantulas geographically, causing the formation of new smaller
sub populations. The reason these small populations lack in
genetic diversity is they don’t have enough individuals to
create a substantial amount of genetic variation (Machkour et
al. 2011 1). This coupled with the Brachypelma vagans aggressive
and cannibalistic nature cause even less genetic variation. This
leads to a great amount of inbreeding which can weaken the
population and make it more susceptible to disease and other
environmental influences.
Many populations of
The Mexican red rump tarantula live inside rural villages. With
the lack of lots of vegetation in soil provides an optimal spot
for these tarantulas to burrow. However many tarantulas have
misleading folklore that causes people to want to exterminate
them. Some of these common myths are tarantulas venom can kill
you, their bite causes flesh to rot and hooves to fall of
livestock and that tarantulas (Perez and Miles, 2009).
To continue reading about Adaptations that
the B. vagans possess, click here.
Home
References