
Habitat
Where does the organism live?
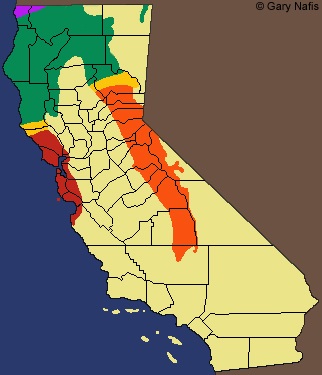
The northern alligator lizard (Elgaria coerulea) is populated mostly in California but ranges
from British Columbia, Montana, and isolated areas of south east Oregon and northwestern
Nevada (Rutherford and Gregory 2003). Amazingly alligator lizards
live in areas ranging from

sea level to about 7,500 feet above sea level
(Telemeco and Addis 2013). These lizards are
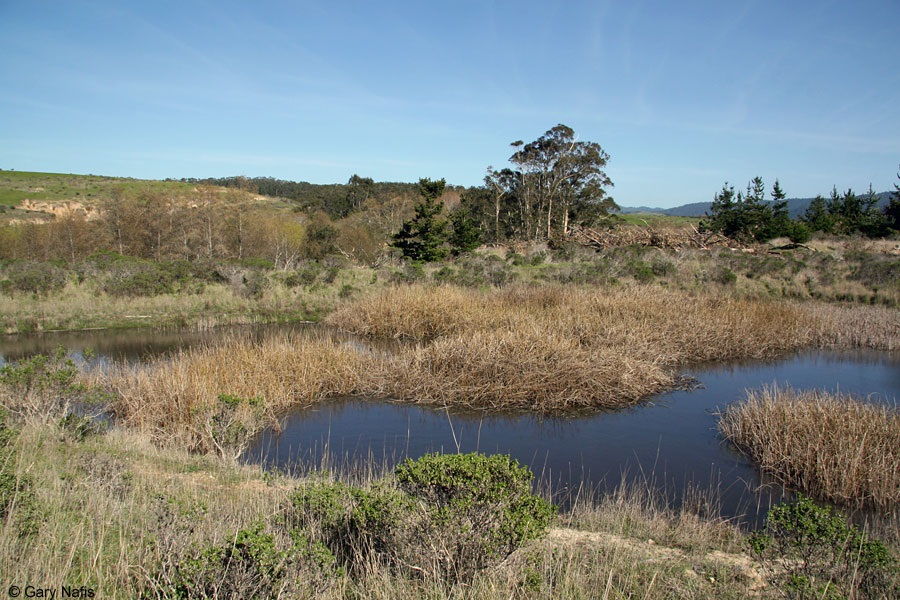
typically found in cooler, wet environments but can
also be found surrounding sunny clearings
(Telemeco and Addis 2013). Counties in California
with large densities of alligator lizards
include: Northern Sonoma County, Monterey
County and also on islands in the San Francisco Bay
and Ano Nuevo island (Lambertz and Graba 2011). Habitats of these cooler environments
include forests, wooded areas along clearings and also coastal marshes (Rutherford and Gregory
2003). These small reptiles often live under debris found in the forests such as under logs, rocks,
bark or any other type of surface cover. The alligator lizard has also been known to inhabit
forest openings that contain grassy cover with low growing bush cover (Lambertz and Graba
2011). This species has adapted to somewhat harsh environments containing rock piles and
rock retaining walls. Due to their slim, snake-like body and small size they can move between
rocks and under woodland debris without being seen. In the
spring, during their mating season,

alligator lizard pairs have been noted to be dwelling in the
rock piles (Lambertz and Graba 2011). Alligator lizards
occupy the same habitat during the summer months as well
as in the winter during hibernation, resulting in no seasonal
migration (Rutherford and Gregory 2003). Without long
distance seasonal migration alligator lizards are at a lower
risk of being killed by predators or other hazards. These
lizards have also been found in residential areas living in man-made rocky formations and under
landscaping such as shrubs, bushes and also under wood boards. This specific lizard does not live
alone and most coexist with a variety of other species in the same environment. This species
interacts with the closely
related southern alligator lizard
 along with snakes, shrikes, some bird
along with snakes, shrikes, some bird
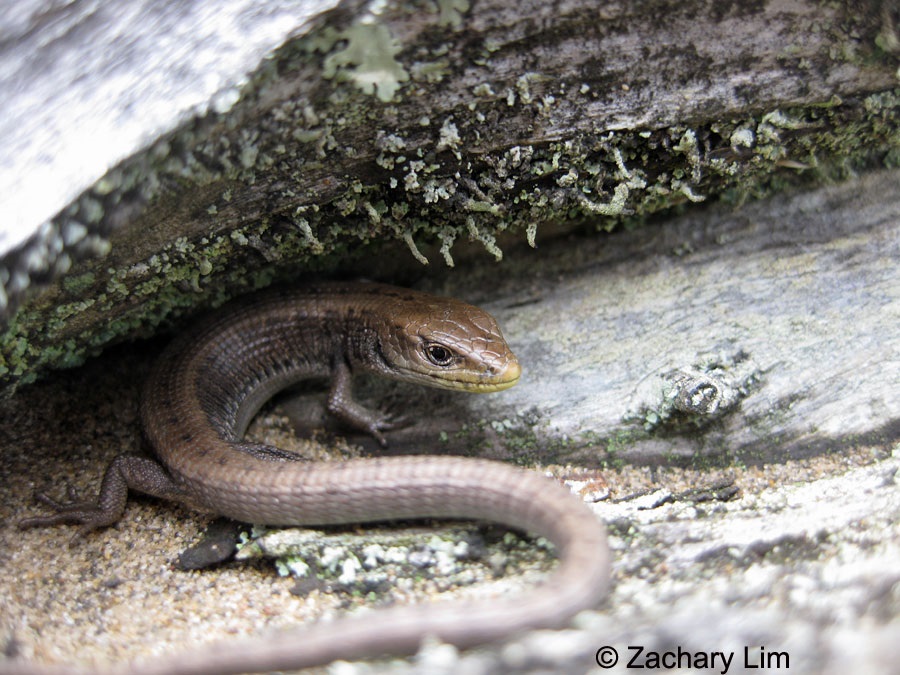
species and also humans. Western skinks specifically inhabit the
same habitats as alligator lizards year round. During the spring,
summer, fall and winter months these skinks can be found under
rock piles and beneath vegetation. This indicates that skinks
exhibit no seasonal migration as well, living in the same location
year round.
How is the northern alligator lizard distributed?
Elgaria coerulea is mobile and distributes itself across a large part of the western United States
including parts of British Columbia and also islands off the coast of California. Northern
alligator lizards are not seasonal migrators and typically live in the relatively same spot year
round. Because of the temperate, cool climate they live in finding food and obtaining nutrients
is not a dire concern for these lizards. These lizards are capable of swimming so they are
not restricted to just land and may spread to islands or other water bound areas. As the name
suggests, they are reptiles so they are active during the day and tend to be inactive during the
colder months during winter.