Classification
Hell Creek Cave Crayfish (Cambarus
zophonastes)
Domain: Eukarya
Organisms are multicellular with nuclei and membrane-bound
organelles such as the mitochondria, golgi apparatus,
endoplasmic reticulum, and more. There are unicellular and
multicellular eukaryotes. Nearly all organisms we are familiar
with are eukaryotes such as the cute
Leapord Cat and the
Giant River Otter.
Kingdom: Animalia
All organisms in the kingdom are multicellular eukaryotes,
ingestive heterotrophs. They have some sort of support
structures, with organized organelles, they have specialized
cells and reproduce sexually. Animals include the charismatic
megafauna such as the
Honey Badger or the
Kodkod.
Phylum: Arthropoda
They are animals that have an exoskeleton, a segmented body, jointed appendages,
compound eyes, and specialized mouth parts. Arthropods used
their hard exoskeletons for protection, and also attachment
sites for muscles. Other Arthropods include the
Tasmanian Cave Spider and the
Exploding Ant.
Class: Malacostraca
These are animals that have a shell for
an exoskeleton that molts, it contains more animals than any
other class. Other animals in the Malacostraca are crabs,
lobsters, shrimp, krill, woodlice, scuds, and the
Mantis Shrimp.
Order: Decapoda
Those in the Malacostraca that have 10 legs. Most of the
Decapoda are scavengers, with 15,000 different species, over
half being crabs, and the shrimp and anomura making up the bulk
of the other half. A cousin of the crayfish, also a member of
the Decapoda is the interesting
Alabama Cave Shrimp.
Family: Cambaridae
Family of freshwater crayfish, it is the largest of the 3
familis of freshwater crayfish with over 400 species. The
majority of the species belonging to the family are found in
North America.
Genus: Cambarus
Freshwater crayfish that are found in North
America, most are small crayfish found in slow moving water.
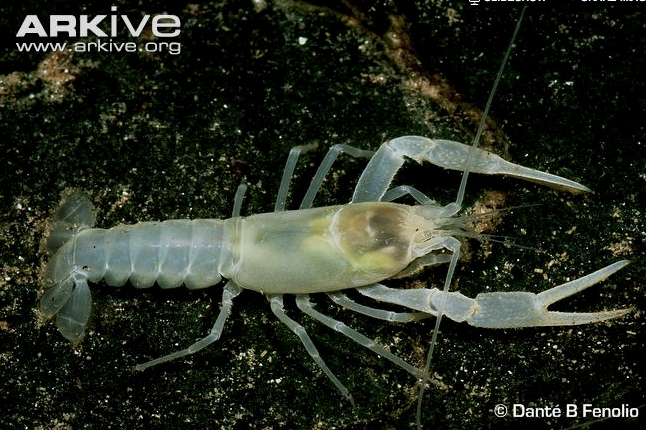
Species: Cambarus zophonastes
Hell Creek Cave Crayfish. The
scientific name means a crayfish that lacks pigment in the body
or the eyes. This is the lovely character that you will be
learning all about on our page.
The Cambaridae family is made up of 12 different freshwater crayfish genera. 3 of the 12 genera, Cambarus, Orconectes, and Procambarus, are species rich, which means that they are comprised of 90+ species. The Cambarus genus is divided into multiple subgenera that are based on the chelae morphology. The Jugicambarus subgenus is what causes the Cambarus genus to be nonmonophyletic. That is because it is not geographically located within the main distribution of Cambarus species, which is mainly in the southern part of the Appalachian Mountains. (Breinholt, 2012)
This is a phylogenetic tree of a number of the
Cambarus species. The
species that are closely related to it are also
cave crayfish. A feature
that they share is that they all lack pigment.
Some of these species include Cambarus subterraneus and Cambarus
aculabrum. They are all
in different regions of the country but all have very similar habitats.

.png)