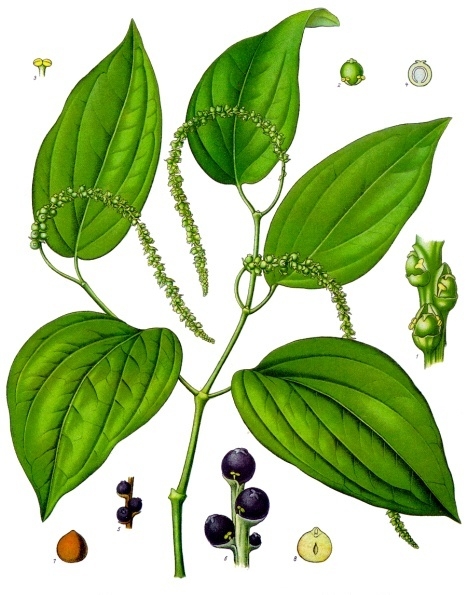
Domain: Eukarya
Kingdom: Plantae
Phylum (Division): Magnoliophyta
Class: Magnoliopsida
Order: Piperales
Family: Piperaceae
Genus: Piper
Species: Piper nigrum
Classification Definitions
Eukaryote: Members of this domain all possess certain common traits. Cells of these organisms possess a true nucleus and membrane bound organelles.
Plant: Kingdom belonging to the eukaryotic supergroup Archaeplastida. Organisms in this kingdom are multicellular, contain celluose as a structural element of their cell walls, and contain chloroplasts which allow the organisms to conduct photosynthetic activity.
Magnoliophyta ("Angiospermae" or "flowering plants"): This division of Kingdom Plantae contains organisms who produce covered seeds, flowers, endosperm, and stamens.
Magnoliopsida ("Dicotyledons, Dicots"): Members of this class produce an embryo with paired cotyledons and possess a net-like veination structure in their leaves. Piper plants are neither monocot or eudicot (true dicotyledon).
Piperales: Order of dicot flowering plants containing herbs, shrubs, and small trees. Members of this order have small flowers clustered together in cone shaped structures.
Piperaceae("Pepper" family): Family of Piperales who generally live in warm, tropical, foliated and shady habitats.
Piper: Genus of plants that contains pepper vines. This term comes from the ancient Tamil word pippali meaning long pepper. The word "pepper" has been applied to similarly spicy plants over history, resulting in the naming of common chile "peppers" and similar members of the genus Capsicum which contain the spicy hot chemical capsaicin.
Piper nigrum: Specific species known commonly as black pepper which derives its name from the Latin words for ""pepper" and "black."
Cladistic Information
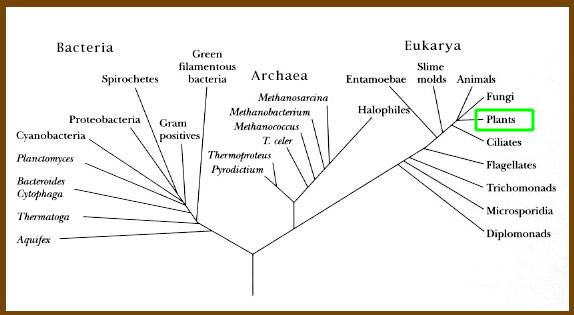
Above: The three domains that include all life are the most general of all taxonomic groupings. This diagram shows the general placement of all life into these three Domaines, and also indicates shared ancestors between organisms. Plants can be found highlighted in green in the Eukarya domain.
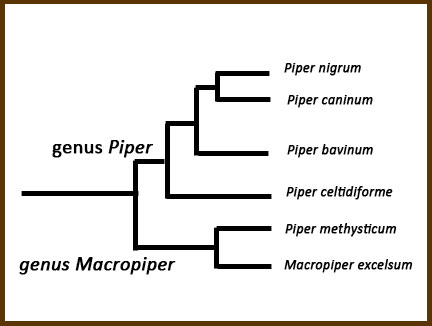
Above: This cladistic tree shows some of the members of the genus Piper that are most closely related to Piper nigrum.
For information about the habitat of Piper nigrum, click here
Design: Adam Haggerty - UW La Crosse - Last modified 4/16/2011