Classification
Domain: Eukarya
Kingdom: Animalia
Phylum: Chordata
Class: Mammalia
Order: Carnivoria
Family: Ursidae
Genus: Ursus
Species: Ursus arctos
Eukarya
The grizzly bear is in the domain Eukarya. It is
classified in this domain because it is a Eukaryote. All Eukaryotes have
cells, a nucleus, and other membrane bound organelles (Wallace, 1997).
Animalia
They are in the
kingdom Animalia because they are eukaryotic, multicellular, heterotrophic,
motile, and they lack rigid cell walls (Wallace, 1997).
Chordata
They are in the
phylum Chordata because they are deuterostomes (develop anus-first) and they
possess a notochord and a tail (Wallace, 1997).
Mammalia
Grizzly bears are in the class Mammalia because they have hair,
three middle ear bones, sweat glands (and mammary glands if they are
females), a four-chambered heart and a neocortex. The neocortex is a portion
of the brain located in the outer layers of the cerebral cortex involved in
reasoning, sensory perception, thought and language (Wallace, 1997).
Carnivoria
They
are in the order Carnivoria because they are flesh-eating organisms with
sharp teeth and claws (Wallace, 1997).
Ursidae
They are in the family Ursidae because they are caniforms (dog-like
carnivorians) with long snouts and non-retractile claws (Wallace, 1997).
Ursus
They are in classified in the genus Ursus, because they are a type of bear
with large bodies, long hair, and short legs and tails (Wallace, 1997).
Ursus arctos
The scientific name for the grizzly
bear, Ursus arctos, comes from the Latin word, ursus, meaning
bear and the Greek word, arctos, also meaning bear (Wallace, 1997).
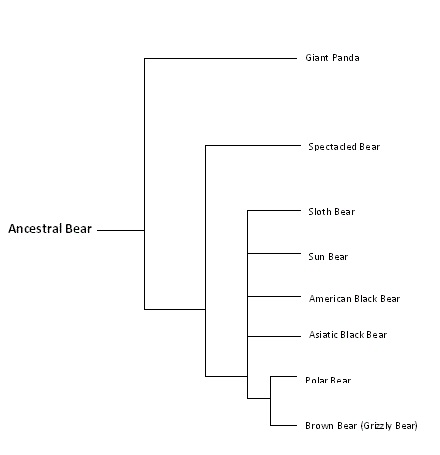
The closet relative to the grizzly
bear is the
polar bear. The grizzly and the polar bear are sister taxa. Sister
taxa simply mean that they are the closest living relatives of each other.
The phylogenetic tree below is based on the Ursidae family. The members of the
Ursidae family are all caniforms, as stated earlier. Polar bears recently
diverged from grizzly bears, approximately 4-5 million years ago (Phylogeny,
2011).
Marissa Hogan
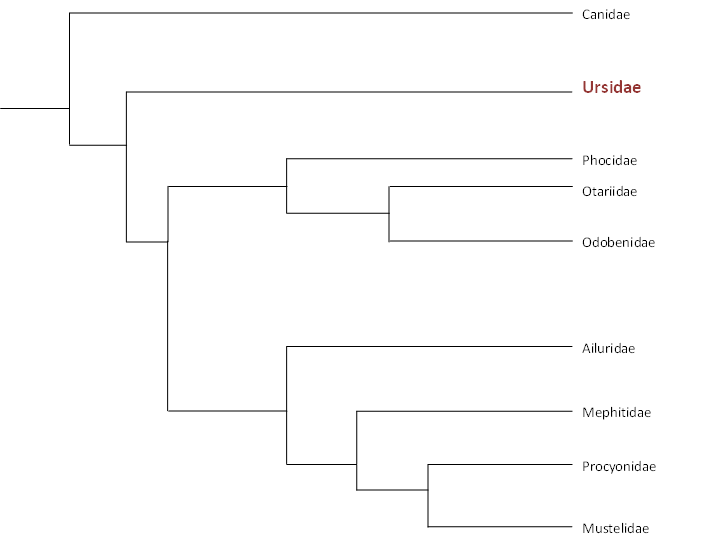
The next tree shows the phylogeny of the order Carnivora. This tree shows that the Ursidae are most closely related to the Canidae. Members of the Canidae include domestic dogs, wolves, foxes, jackals, and coyotes (Westbroek, 1998).
Marissa Hogan