|











| |

|
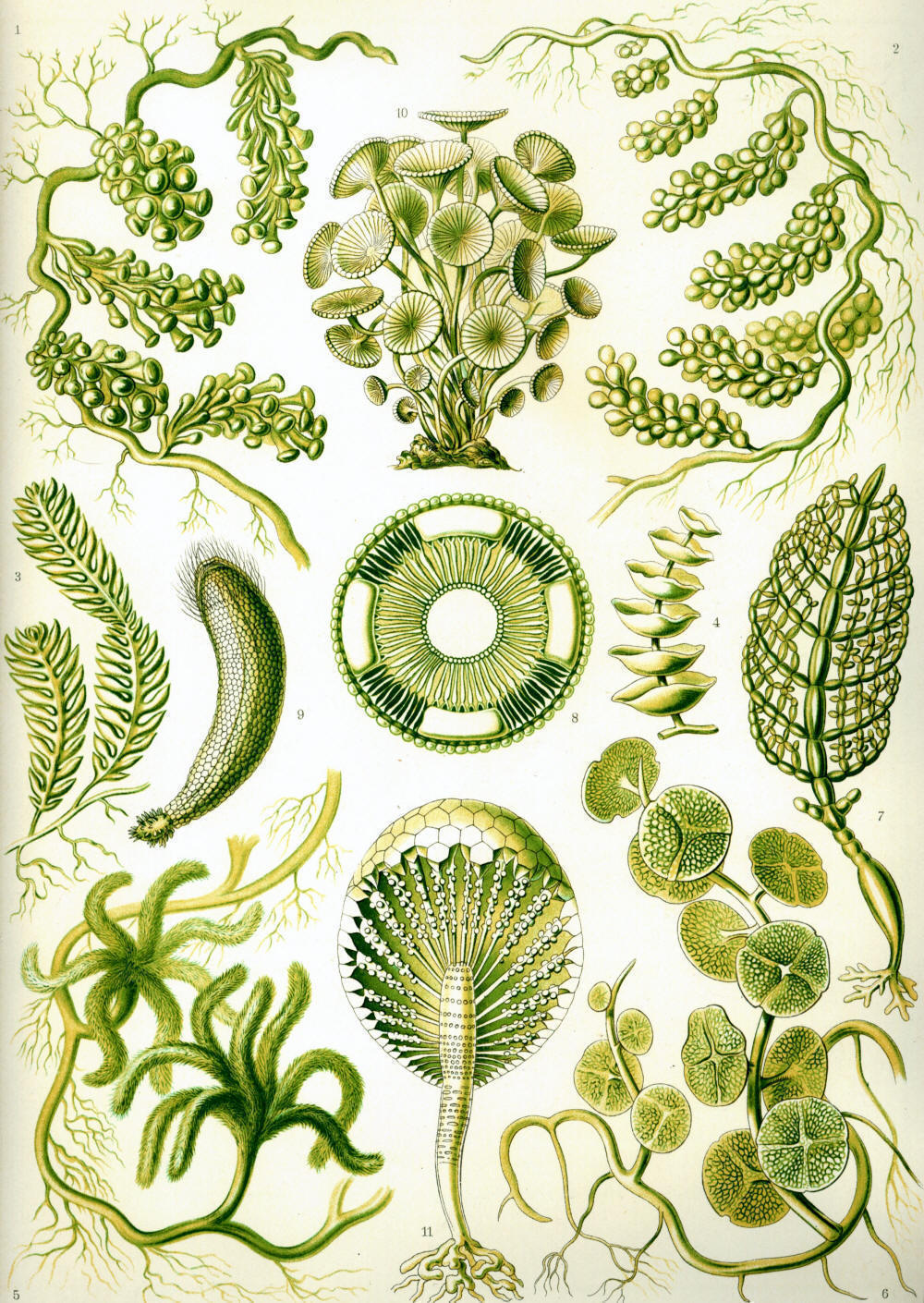
Domain
Eukarya
Chlamydomonas is part of the domain Eukarya for many reasons, all the
species of its genus posses membrane bound organelles such as a nucleus,
chloroplast, mitochondria, and a pyrenoid. Its flagella, like other
eukaryotes, consist of an axoneme with microtubules in a 9 +
2 configuration instead of a being powered by different rings within a
basal body like most prokaryotes, the flagella are powered by different dynein protein motors. Furthermore
Chlamydomonas has DNA in the
structure of linear chromosomes while prokaryotes possess circular DNA. |
top
|
Kingdom
Protista
Chlamydomonas is part of the kingdom Protista for many
reasons one being that they require some type of a water based
environment in forms as marine water, fresh water, moist soil,
or even snow. Chlamydomonas also classifies as
a protist because it is aerobic like other protists which can either
have mitochondria to do cellular respiration or have chloroplast to do
photosynthesis, an advantage that Chlamydomonas has however is the
ability to do both. |
top
|
Phylum
Chlorophyta
Chlamydomonas is organized into the phylum Chlorophyta
for many reasons, one being the fact that most members of Chlorophyta
including Chlamydomonas are photosynthetic and either multi-cellular or
single celled. Also Chlamydomonas doesn't store its food as glycogen but
as starch. Chlamydomonas like must members of this group contains
chlorophyll with pigments a,b, and
b
carotene. |
top
|
Class
Chlorophyceae
Chlamydomonas is a member of the class Chlorophyceae mainly because most
members of this class possess flagella arranged in a certain way,
Chlamydomonas having an arrangement of two flagella position next to one
another at the cell's apex which it uses in a breaststroke like motion. Another property
members of this class have is that they all have a haploid life cycle in
which the only diploid structure is a zygote, which develops into a zygospore to withstand harsh growth conditions.
top
|
|
Order
Volvocales
Chlamydomonas belongs to this order because like most the other members
Chlamy is a unicellular flagellated cell. Though many of the other
members of this order exist is colonies, Chlamydomonas is a solitary
cell. Also most members of this order have two flagella arranged in a
specific way at the apex of the cell body.
top
|
|
Family
Chlamydomonadaceae
Chlamydomonas falls into the family Chlamydomonaceae because it
possesses crystalline cell wall components instead of having a cell wall made
of cellulose Chmaydomonas has a cell wall mostly composed of
hydroxyproline-rich glycoproteins.
top
|
|
Genus
Chlamydomonas
All members of the genus Chlamydomonas are unicellular and also
capable of producing flagella. One of the unique features the genus
Chlamydomonas possesses is that they contain protein ion channels that
are capable of being directly activated by photons of light.
top
|
|
Species
Chlamydomonas reinhardtii
C. reinhardtii is a very popular single celled
algae which classifies into all the groups above, but a couple
interesting things at the species level is that C. reinhardtii
primarily does photosynthesis but is able to become a heterotroph in the
absence of light by using acetate as a source of carbon.
top
|
back to top
|














.jpg)