|
|
|
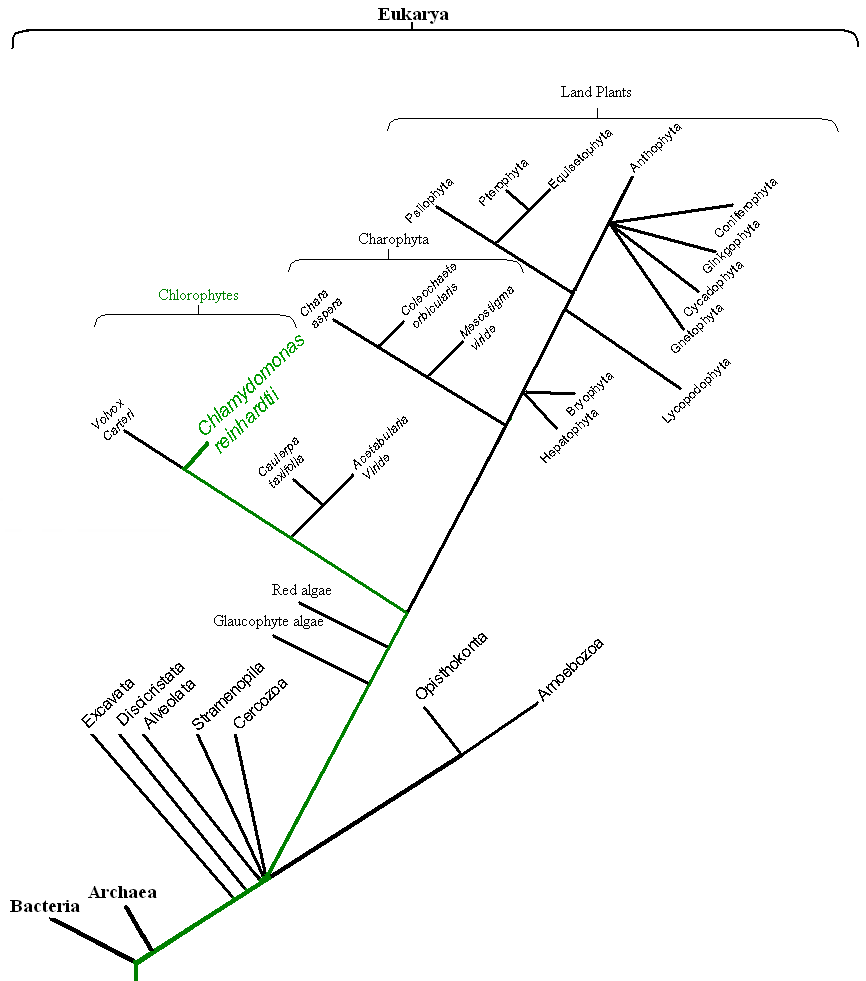
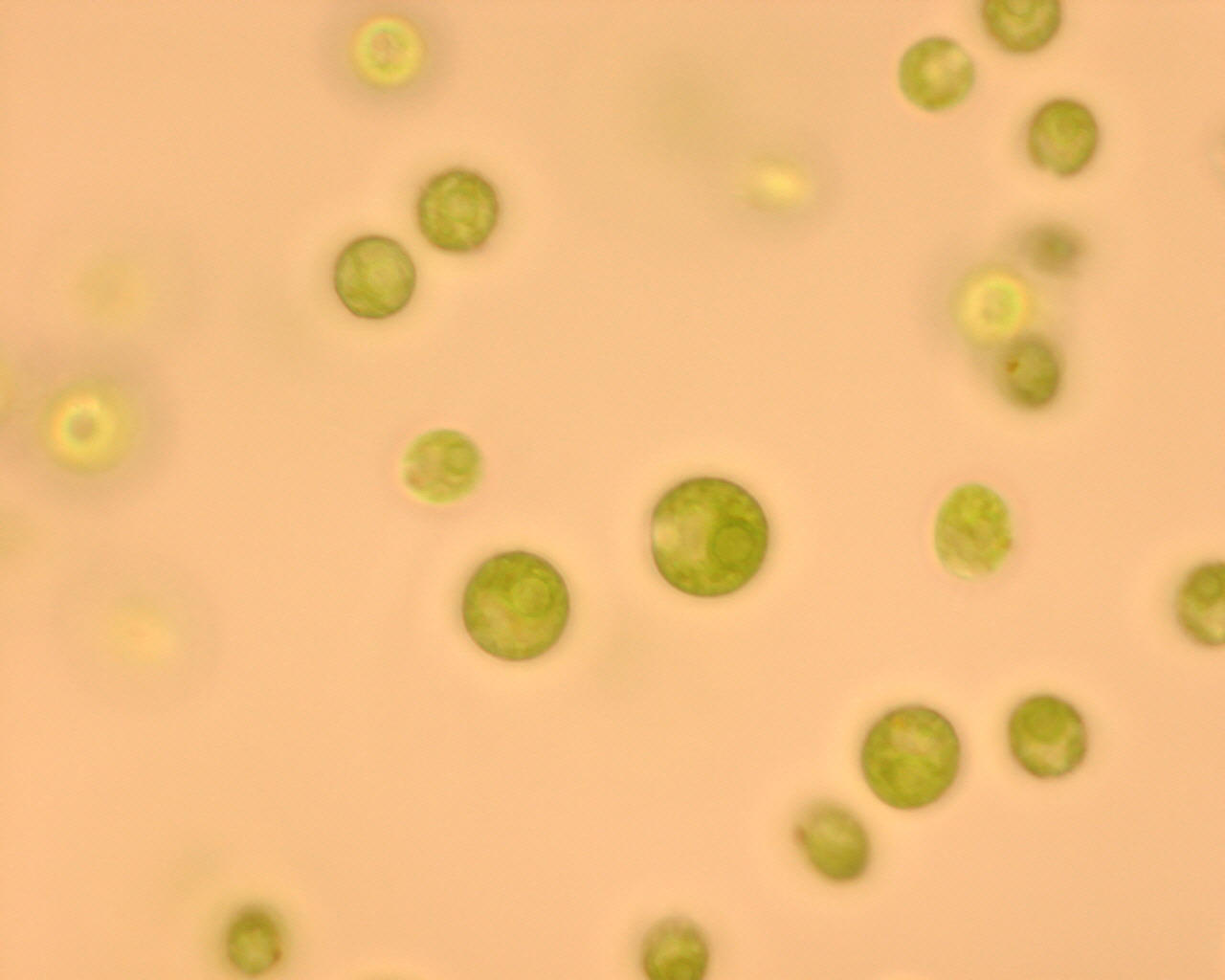
In the order Volvocales the genus Chlamyodomonas is closely related to other solitary cells like itself such as the genus Carteria which is very similar in body structure except for the addition of two more flagella for a total of four flagella at its apex as well as having more flagella this organism also possesses multiple pyrenoids. The Chlorogonium genus is closely related but with an elongated cell body, Phacotus is also similar except with a distorted cell wall structure.
|
 |
|
Colonial organisms related to Chlamydomonas under the order Volvocales include the very similar genus Pandorina these cells have a very similar cell structure as Chlamydomonas with two flagella, pyrenoids, an eyespot, a cup shaped chloroplast, and contractile vacuoles the only difference is they form colonies of 8,16, or even 32 cells. A unique feature about the genus Pandorina is that the cells within the colony show signs of differentiation with the formation of different size eyespots among cells. Another close relative of Chlamydomonas are members of the genus Gonium, this genus forms colonies of 6 or 18 cells within a gelatinous sheath and are able to move together productively. One of the largest colony forming relatives of Chlamydomonas is the genus Volvox which can create colonies as large as 5,000 cells! During reproduction the cells of the daughter colonies have their flagella pointed inward and right before they are released they go through an inversion pointing their flagella outward in order to become motile. |














.jpg)