|
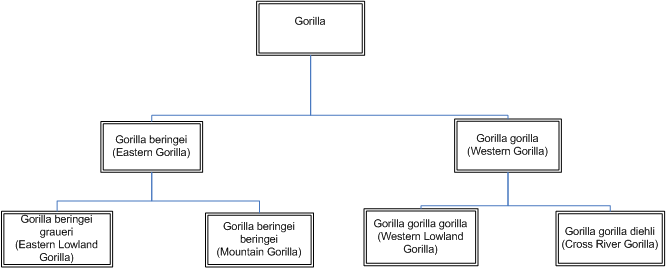
Domain: Eukarya Gorilla cells have membrane-bound organelles with specialized functions and their genetic material is held in a nucleus. Kingdom: Animalia Gorillas are multicellular heterotrophs whose cells lack cell walls and tissues form organs and organ systems. Phylum: Chordata Gorillas have 3 germ layers, a well developed coelom, a segmented body, a single nerve chord, a closed blood system, a closed digestive system, and an endoskeleton comprised of bone. Subphylum: Verbrata Gorillas have a vertebral column that is part of a bony endoskeleton that has muscles, appendages, and a cranium. They also have an inner and outer epidermis, a digestive system with advanced organs, a heart with 4 chambers, and a blood system that uses hemoglobin. Class: Mammalia Gorillas have 3 middle ear bones, the hammer, anvil, and stirrup, hair on the outer epidermis, and the females have mammary glands that produce milk. Order: Primates Gorillas have separate and highly mobile radius and ulna in the forearm and tbia and fibula in the hind leg. They also have an opposable hallux and pollex which is commonly referred to as the thumb and the big toe. Suborder: Haplorrhini Gorillas have paired downward directed nasal openings, an upper lip that isnít attached to the nose or gum and a high brain to body size ratio. Family: Hominidae Gorillas have robust bodies and well developed forearms. They also have a large braincase and their teeth consist of upper and lower molars, broad incisors, and canines. Genus: Gorilla Gorillas are the largest primates whose lower jaw portrudes out farther than their upper jaw. Species: Gorilla beringei Eastern Gorillas are large hominids with a flat nose with large nostrils and a bare face, hands, feet, and breast. Subspecies: Gorilla beringei beringei Mountain Gorillas have longer and darker hair and longer jaws and teeth. They also have slightly shorter arms and their feet most resemble humans. Gorilla beringei graueri Eastern Lowland Gorillas are the largest of the 3 subspeices and has a stocky body large hands and a short muzzle. They have longer teeth, a stronger jaw, and a broader torso. They also have small ears and large nostrils and their hair is all black. Bwindi Gorilla Bwindi Gorillas do not have a scientific name and are recently separated from the Mountain Gorillas. They share many of the same characteristics and behaviorisms as Mountain Gorillas.Phylogenetic Tree
|