Species Interactions
The Paralithodes camtschatica is surrounded by an environment full of organisms. Because the individual crab is so different in each stage of development, the relationships to other species differ to each stage. Also to keep in mind is the different environments the crab lives in during several periods in its life and the types of organisms that live there as well.
 The larvae crab lives in shallow water,
swimming around among the plankton. The zoea larvae use the plankton as their
food source as well as protection, the plankton keeping the zoea away from
predators such as the filter feeding organisms. Organisms that filter feed the
seawater tend to stay away from the plankton infested areas, thus not taking in
the zoea in the plankton.1
Although predators of plankton, the zoea are also prey to the many other animals
living around them, including aquatic worms, sea urchins, and barnacles.
Aquatic worms, such as the Carcinonemetridae family, have been found to also
feed on many decapod eggs, thus given the name, the Nemertean Egg Predators.
They are capable of doing so because of the crab's external fertilization.2
The larvae crab lives in shallow water,
swimming around among the plankton. The zoea larvae use the plankton as their
food source as well as protection, the plankton keeping the zoea away from
predators such as the filter feeding organisms. Organisms that filter feed the
seawater tend to stay away from the plankton infested areas, thus not taking in
the zoea in the plankton.1
Although predators of plankton, the zoea are also prey to the many other animals
living around them, including aquatic worms, sea urchins, and barnacles.
Aquatic worms, such as the Carcinonemetridae family, have been found to also
feed on many decapod eggs, thus given the name, the Nemertean Egg Predators.
They are capable of doing so because of the crab's external fertilization.2
 When the red king crab begins its megalops
stage, it migrates to the ocean floor. These juvenile crabs are still
susceptible for much predation, thus hiding under rocks, in crevices and
trenches, and using the kelp to keep hidden from predators.3 They have a
predatory relationship with the kelp, the crab not only receives protection, but
also the kelp is part of the juvenile king crab’s diet. The small crabs start
becoming predators like the adult forms, feeding on kelp, sea stars, clams,
muscles, barnacles, etcetera. The megalops crabs are still under much
predation, being easy prey for many fish, example being cod, as well as other
crab species and invertebrates.4
When the red king crab begins its megalops
stage, it migrates to the ocean floor. These juvenile crabs are still
susceptible for much predation, thus hiding under rocks, in crevices and
trenches, and using the kelp to keep hidden from predators.3 They have a
predatory relationship with the kelp, the crab not only receives protection, but
also the kelp is part of the juvenile king crab’s diet. The small crabs start
becoming predators like the adult forms, feeding on kelp, sea stars, clams,
muscles, barnacles, etcetera. The megalops crabs are still under much
predation, being easy prey for many fish, example being cod, as well as other
crab species and invertebrates.4
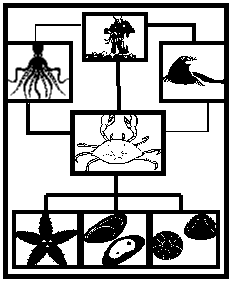 The adult red king crab is also a well known
predator of the echinoderms, sponges, worms, mollusks, and small fish. Because
of the red king crab’s defensive carapace and claws and large size, they have
fewer predators then megalops. Predators of the king crab include the octopus,
seal, and humans.5 The Alsakan king crabs also come into contact with a special
type of barnacle, the Briarosaccus callosus, which acts as a parasite, causing
“sterilization and reduced growth” to the king crab.6
Also, the adult king crab uses kelp and other substrates as protection during
mating and molting, when their hard carapace is gone.7
The adult red king crab is also a well known
predator of the echinoderms, sponges, worms, mollusks, and small fish. Because
of the red king crab’s defensive carapace and claws and large size, they have
fewer predators then megalops. Predators of the king crab include the octopus,
seal, and humans.5 The Alsakan king crabs also come into contact with a special
type of barnacle, the Briarosaccus callosus, which acts as a parasite, causing
“sterilization and reduced growth” to the king crab.6
Also, the adult king crab uses kelp and other substrates as protection during
mating and molting, when their hard carapace is gone.7