Prickly Pear Cactus (Opuntia chlorotica)
Reproduction
Reproduction in the prickly pear cactus can happen either by sexual
or asexual means.
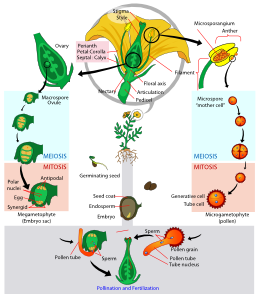
In sexual reproduction pollen is produced in the anther (a structure on the stamen of the flower) and the egg is formed in the ovary. An anther consists of microsporangia that contain diploid cells called microsporocytes. after undergoing meiosis these microsporoctes create microspores. The microspores go through mitosis producing two haploid cells that, along with the spore wall make up a pollen grain. The female gametophyte is produced when one cell in the megasporangium of the ovule (a structure in the ovary) undergoes meiosis, producing four haploid cells called megaspores. however, three of these megaspores break down, leaving only one. This megaspore continues to grow, and its nucleus divides three times to create eight haploid nuclei in one cell. This megaspore and is part of the ovule which becomes the seed after fertilization. Fertilization happens when a pollen grain is transferred to the stigma (a structure on the flower that gives way to the ovary) and produces a pollen tube that grows down to the ovary and releases sperm. The ovule becomes the seed and the ovary becomes a fruit that protects the seeds.
Asexual reproduction in the prickly pear cactus is called vegetative reproduction or vegetative cloning. This happens when part of the mature parent plant is detached and develops into a new plant.