Alabama Cave Shrimp - BIO203
The Classifieds:
Domain (Eukarya)
Members of the Domain Eukarya have a nucleus and other
organelles.
Major Clade (Opisthokonta)
All members within the major clade, Opisthokonta, have a
posterior flagellum that pushes through the water.
Kingdom (Animalia)
The group, Animalia, is multicellular, heterotrophic and ingests
food first then digests it (For more information see
Canadian Marine Biology).
Some examples of animals which are relatives to the Alabama Cave shrimp
are
Polyrhachis lamellidens and
Hippocampus
kelloggi.
Phylum (Arthropoda)
The phylum, Arthropoda, consists of organisms with exoskeletons
made of chitin, joined appendages, and the ability to molt
(Canadian Marine Biology). Two organisms that join the
Palaemonias alabamae in this phylum are the
Metrius contractus and
Harpaphe haydeniana.
Class: Malacostraca
The class, Malacostraca, is characterized by a body made up of
twenty segments (Canadian Marine Biology). A few other
closely related organisms are
Allogona
profunda and
Carychium
exiguum.
Order: Decapoda
Decapod is the order of this species due to having ten legs and
a thick shield on either the entire body or a piece of the back
(Canadian Marine Biology). Another example of a decapod is
Oregonia gracilis.
Family: Atyidae
The phylogenetic information is currently being updated for the
family Atyidae. After looking through many different scientific
articles, the old features for this groups are being challanged. Some of
the old features to distinguish the family included the way the eyes
were placed, the type of spines, and sizes.
Genus: Palaemonias
The closest relative to the Alabama Cave Shrimp is the Kentucky
Cave Shrimp, Palaemonias ganteri (Cooper and Cooper 2010). One
similarity I noticed between both the Alabama Cave Shrimp and
the Kentucky Cave Shrimp is that they are both colorless (Cooper
and Cooper 2010). The genetic components linking these two
organisms are not yet known (Cooper and Cooper 2010).
Species: Palaemonias alabamae
Parts of the name can be broken apart to show meaning about the
organism. Alabamae refers to the
habitat the organism lives in
which is the state of Alabama and "Paleo" means old.
Phylogenetic Trees can help to better understand a species
relationship to other organisms. Please see the trees below to get a
better idea of the Alabama Cave Shrimp's relatives.
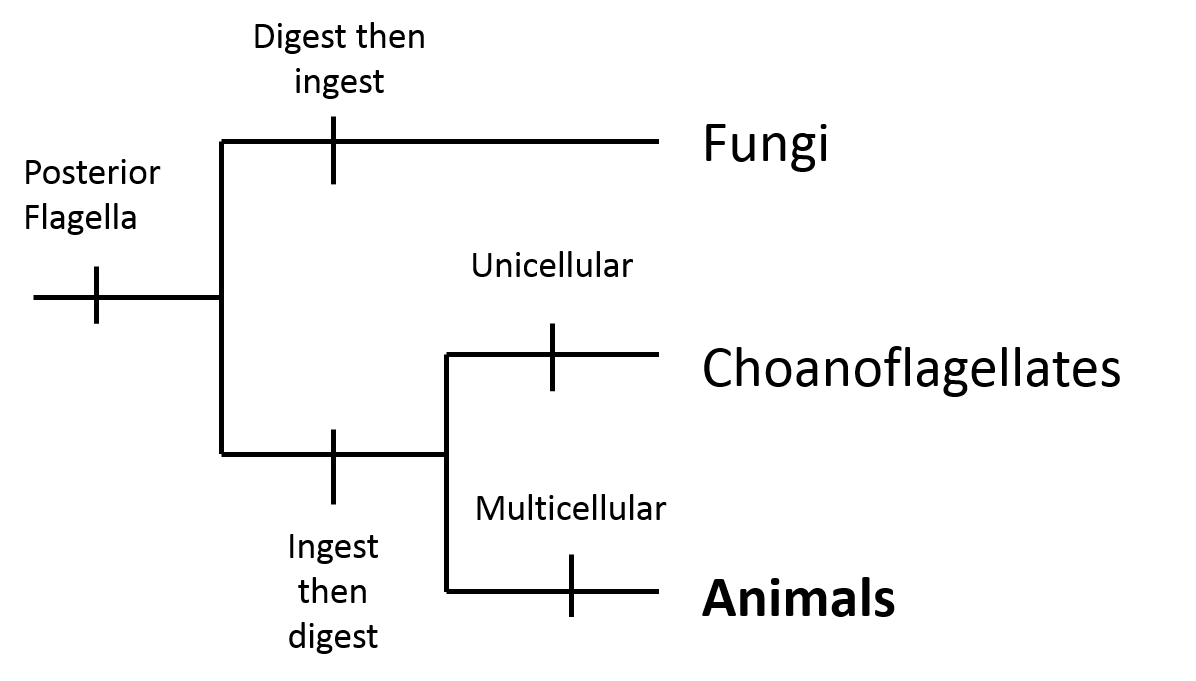
In the phylogenetic tree in figure one, the Alabama Cave Shrimp
belongs to the major clade Opisthokonta. Within the clade
Opisthokonta are the choanoflagellates, fungi and animals. An
example of a fungus is
Psilocybe cubensis.
Figure 1. Major Clade Opisthokonta Phylogenetic Tree.
In Figure two, the phylogenetic tree is of the genus Palaemonias
which is made up of the Kentucky Cave Shrimp and the Alabama Cave
Shrimp. As you can see, these two species share many similarities but
also differences.
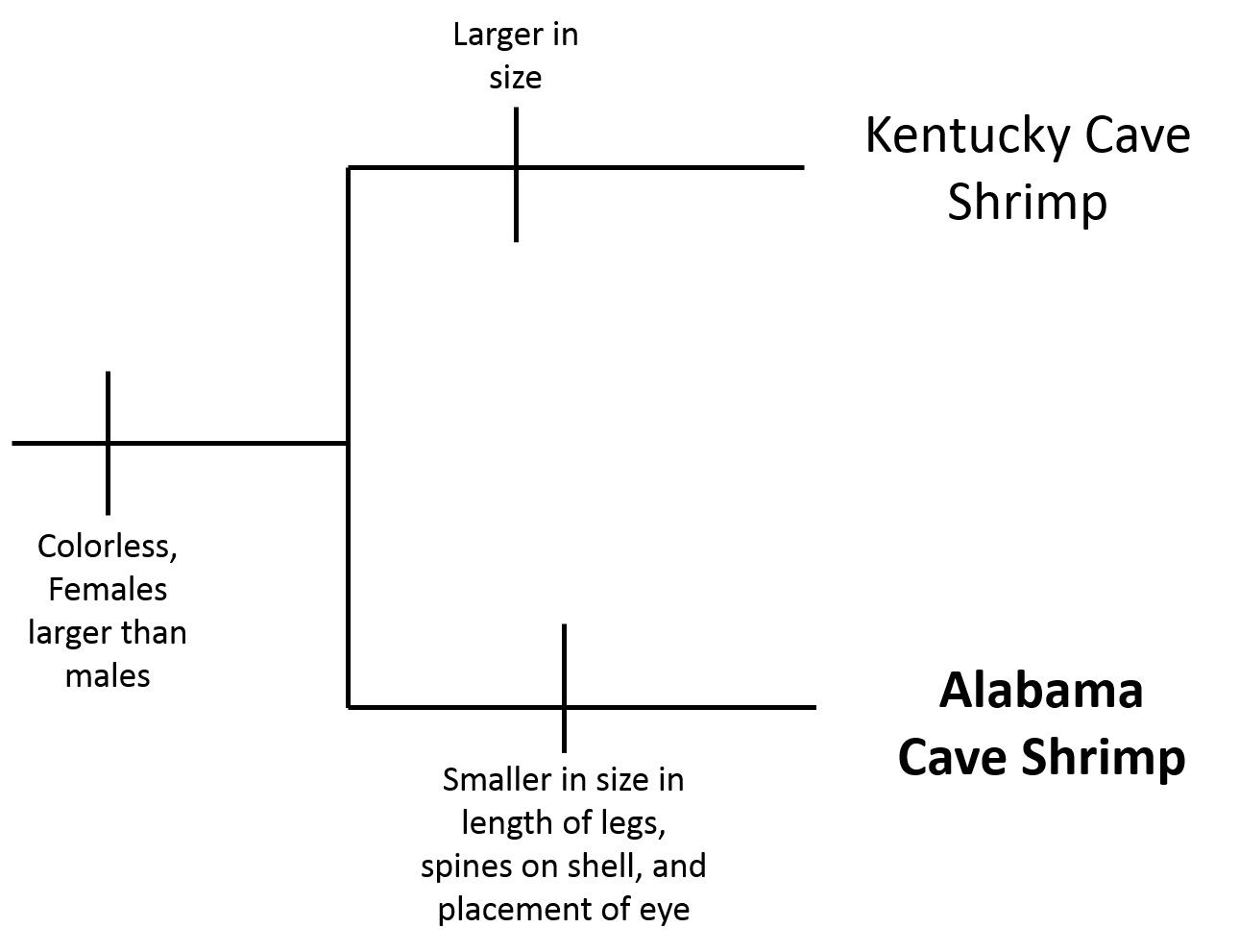
Figure 2. Genus Palaemonias Phylogenetic Tree
To see where on earth Palaemonias alabamae can be found, continue on to Habitat.