Classification
DOMAIN: Eukarya
KINGDOM: Animaila
PHYLUM: Chordata
CLASS: Aves
ORDER: Passeriformes
FAMILY: Cinclidae
GENUS: Cinclus
SPECIES: Cinclus mexicanus
________________________________________________________________
Cinclus
mexicanus
Understanding the classification of the
American Dipper
Domain- Eukarya
The Eukarya domain includes all eukaryotic organisms. These
organisms have membrane bound organelles such as mitochondria and
have a true nucleus unlike organisms of the bacteria domain or
archaea domain. Other eukaryotic organisms include the
Sumatran Tiger and the
Texas Blind Salamander.
Kingdom- Animalia
Kingdom Animalia refers to a wide variety of animals. The kingdom
consists of motile organisms containing an internal cavity for
digesting and ingesting food. The
Blind Cave fish also belongs to kingdom Animalia.
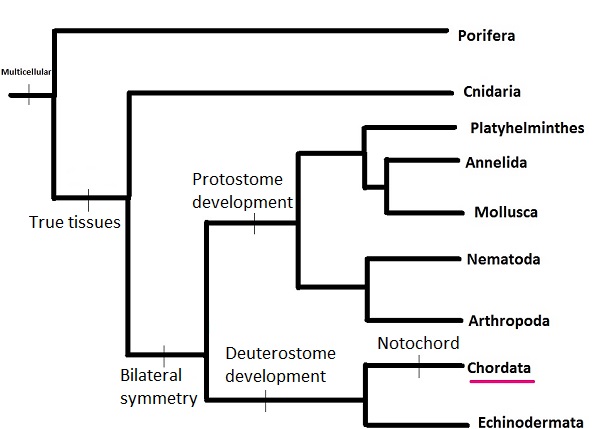
Below is a phylogenetic tree of a few of the different phyla closely
related to the
chordata phylum in the animal kingdom. In addition,
this phylogenetic tree shows the
divergence of the different phyla
of the animal kingdom. This phylogenetic tree was created using
resources from the Spring 2014 Organismal Biology course at the
University of Wisconsin- La Crosse.
Phylum- Chordata
Organisms of the phylum chordata are classified as having bilateral
symmetry, a dorsal
nerve cord (notochord) and a post-anal tail. The
Bar-Headed Goose is also a member of the phylum chordata.
Class- Aves
All members in this class have feathers and lay eggs. Usually the
limbs are paired along with forelimbs that are modified for flying
and with hind limbs for perching, walking, and swimming. All birds
are classified as aves such as the
Yellow-Crowned Night Heron or
Anna's Hummingbird.
Order- Passeriformes
Passeriformes are birds that have three toes that point forward and
one pointing backwards. This toe arrangement is beneficial for
Passeriformes because it helps with perching on different structures
located around their habitat including branches, rocks, cliffs, and
fences. The
Northern Cardinal is also a member of the Passeriform order.
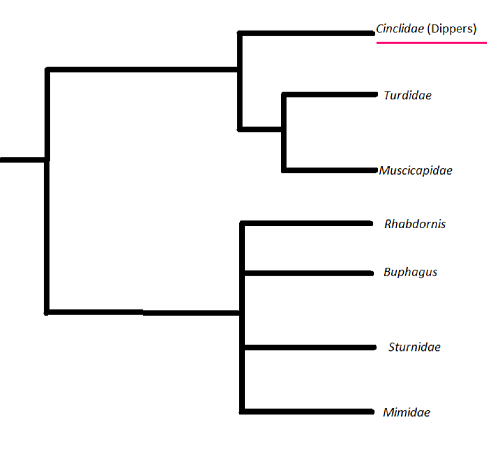
Below is a phylogenetic tree representing the closest relationships the
American Dipper shares with other members of the Passeriformes. The
tree suggests that the American Dipper shares its most recent common
ancestor with both Turdidae and Muscicapidae organisms of the
Passeriform order.
Family- Cinclidae
Birds of the family Cinclidae typically make their nests in areas
near fast-moving water. Members of this family feast on aquatic
insect larvae and small fish found in the aquatic ecosystems they
call home. To learn more about other birds of the Cinclidae family
click
here.
Genus- Cinclus
Members belonging to the genus Cinclus along with other species such
as Cinclus cinclus, Cinclus leucocephalus, Cinclus pallisii, and
Cinclus schulzi. Each of these species of the genus Cinclus are
known as dippers that are small, stout birds known for exerting
“dipping” movements as they stand perched in or near the water.
Species: Cinclus mexicanus
The Latin name Cinclus mexicanus means "American Dipper". The American Dipper earns its name because of its unique "dipping" or bobbing behavior it does while standing in the water or perched on nearby rocks.