Classification
Domain: Eukarya
Kingdom: Animalia
Phylum: Chordata
Class: Mammalia
Order: Carnivora
Family: Mustelidae
Genus: Mustela
Species: Mustela frenata
Domain: Eukarya
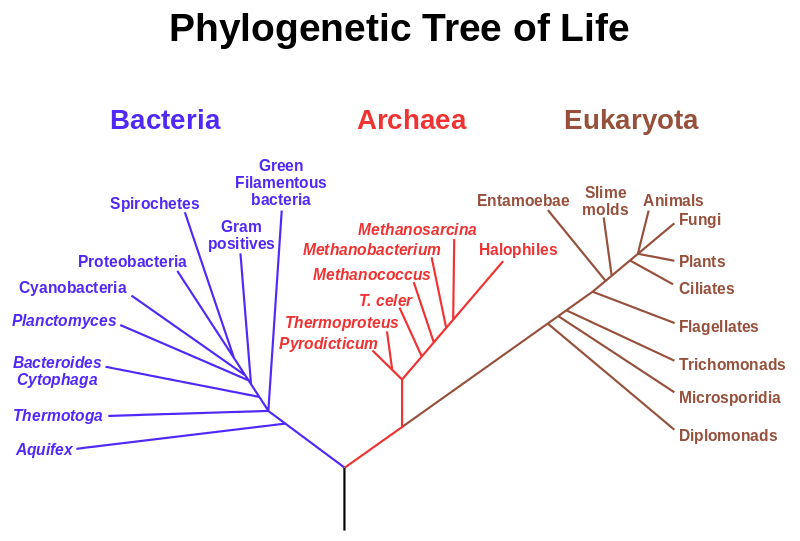
Eukaryotic organisms are characterized by having cells with a nucleus and membrane bound organelles. The Eukaryotes also gave rise to multicellularity which allowed these organisms to increase in size. Eukaryotes share a more recent common ancestor with Archea than with Bacteria as seen in the tree of life below.
Animals are multicellular heterotrophs which means that they can not make their own food. In addition, animals lack structural cell walls in their cells. These organisms live in a huge variety of habitats and are motile in at least part of their life cycle. See how other eukaryotic organisms relate to animals in the tree of life located to the right.
Phylum: Chordata
Chordates are animals that have the adaptions of a nerve chord, which includes vertebrates as well as some organisms closely related to the vertebrates. They exhibit bilateral symmetry which means they have a single plane of symmetry and face their environment in one direction. Chordates have three layers of tissue consisting of a endoderm, ectoderm, and mesoderm making them triploblastic. Their three layers of tissue allows for organ systems within their body. Lastly, members of Chordata are dueterostomes. Duertostomes develop an anus before the mouth in embryonic development.
Mammals are vertebrates that are generally characterized by having body hair. Mammals are also known to care for their young until they reach maturity. They live in a large range of habitats around the world and have a variety of different lifestyles (Animal Diversity Web 2005 B).
Order: Carnivora
Members of Carnivora are mammals that evolutionarily had carnivorous food sources. Many members of carnivora have large molars and strong jaws which they use to tear meat. In addition, they have large brains and relatively short digestive systems. They occupy a wide range of habitat and lifestyles around the world (Animal Diversity Web 2014).
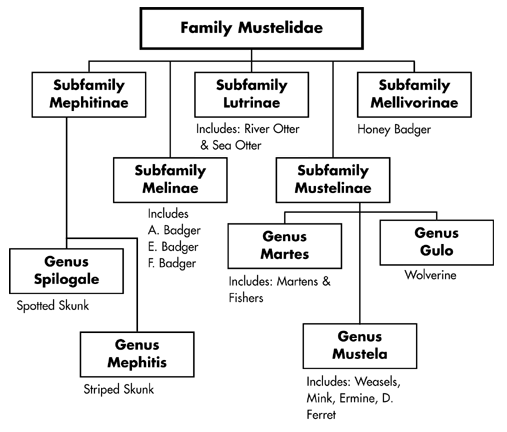
Family: Mustelidae
Mustelidae has 56 species and 22 genera making it
the largest family in the order Carnivora. Mustelidae includes organisms
such as weasels, mink, marten, badgers, and many more. Look at the
Mustelidae family tree to see how these other members of Mustelidae are
related to each other as well as Mustela frenata. This family lives in
all continents except for Autralia and Antarctica. Also, all members
have well developed scent glands for territorial marking or defense
(Animal Diversity We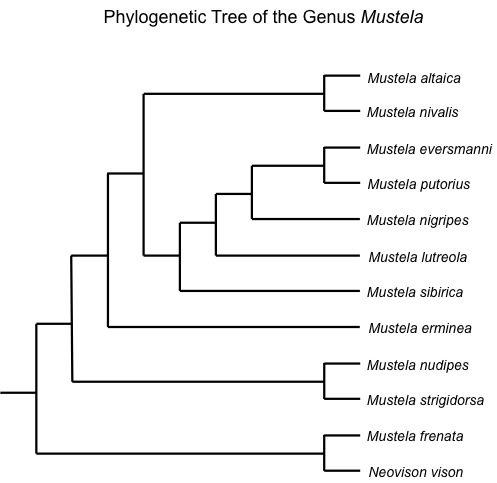 b 2005 A).
b 2005 A).
Genus: Mustela
All members of Mustela have long, slender bodies (Cold 1988). According to the Family Mustelid Tree above, the genus Mustela is very closely related to the genera Martes, which includes martens and fishers, and Gulo, which includes wolverines. The genus Mustela tree to the right shows the relatedness of all extant members within this genus. As you can see, the Mustela genus has a complex evolutionary history.
See Mustela nivalis, which is a close relative of the long-tailed weasel, here!
Species: Mustela frenata
The meaning of Mustela frenata is bridled (frenata) weasel (Mustela) which is referring to its bridle-like markings on its face (Schwartz and Schwartz 2001). Mustela frenata is also known for having the largest range and longest body size in their family (Cold 1998). As seen in the genus Mustela tree, Mustela frenata actually shares a more recent common ancestor with Neovison vison, which is the American Mink, than other Mustelids. Learn more about Mustela frenata's unique features on the rest of the pages on this website!
Back to Homepage Go to Habitat