|
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
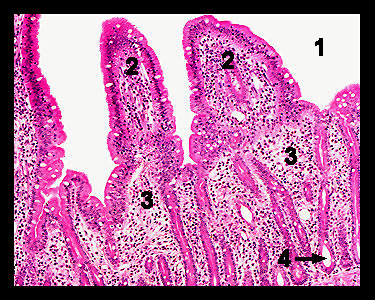
The mucosa contains glands and finger-like projections called villi, which increase the surface area of the intestine for absorption and slow the passage of food through the organ. The lamina propria is composed of loose areolar connective tissue and contains several types of vessels along with a scattering of smooth muscle fibers. Within the core of each villus is a bed of capillaries and a specialized lymphatic vessel called a lacteal, which absorbs fats from the lumen of the small intestine. The capillaries provide nourishment to the epithelial cells surrounding the villi and absorb the products of carbohydrate and protein digestion as well as water and electrolytes. Between adjacent villi are the intestinal glands (crypts of Lieberkühn) that extend deep into the mucosa. The epithelial cells that line these glands secrete a fluid containing mucus that serves as a carrier for the absorption of nutrients from the partially digested food molecules. |
|