Classification
Domain: Eukaryota
Polyodon spathula is classified in the Domain Eukaryota
because it has a true nucleus as well as membrane-bound
organelles.
Kingdom: Animalia
Polyodon spathula
are eukaryotic multicellular organisms that are heterotrophs.
They are also motile (swim) and lack cell walls.
Phylum: Chordata
These American Paddlefish have bilateral
symmetry, segmented bodies, three germ layers (ectoderm,
endoderm and mesoderm), a coelom, a complete digestive tract,
and have the five unique characteristics to the
Chordates--notochord; dorsal, tubular nerve chord; pharyngeal
pouches, endostyle, and postanal tail.
Class: Actinopterygii
This particular class contains ray-finned fishes.
Order: Acipenseriformes
This Order contains primitive bony fish
that have a cartilaginous skeleton, a rostrum (or snout), a
ventrally located mouth, and a
heterocercal tail fin (Figure 2).

Figure 2. Tail of a Paddlefish.
Family: Polyodontidae
The Polyodontidae Family consists
of freshwater fish that have many fossil relatives. A
distinctive feature in this Family is their elongated rostrums
(Figure 3).

Figure 3. A Paddlefish's rostrum.
Genus:
Polyodon
Polyodon is Greek for 'many
toothed' referring to their hundreds of bony, comb-like
protrusions along their gill arch called gill rakers (Figure 4); these gill rakers are specially adapted to help them filter feed for
plankton.
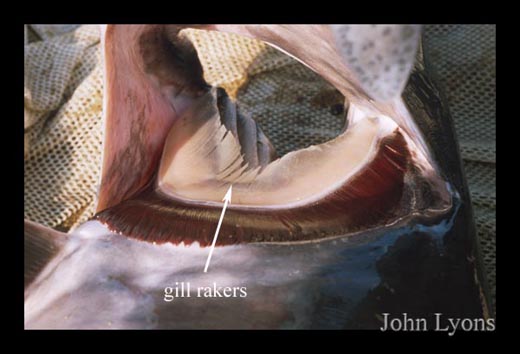
Figure 4. Close-up of gill rakers.
Species: Polyodon spathula
The word spathula
refers to the paddle-like shape of the Paddlefish's rostrum.
Phylogenetic Trees
To have a better understand of where and how the American Paddlefish fits into the grand scheme of things, phylogenetic trees are constructed to better understand the roles of the American Paddlefish. In making these phylogenetic trees, Microsoft PowerPoint was used to construct the tree as well as a lot of time and effort spent in gathering the necessary information to construct the trees.
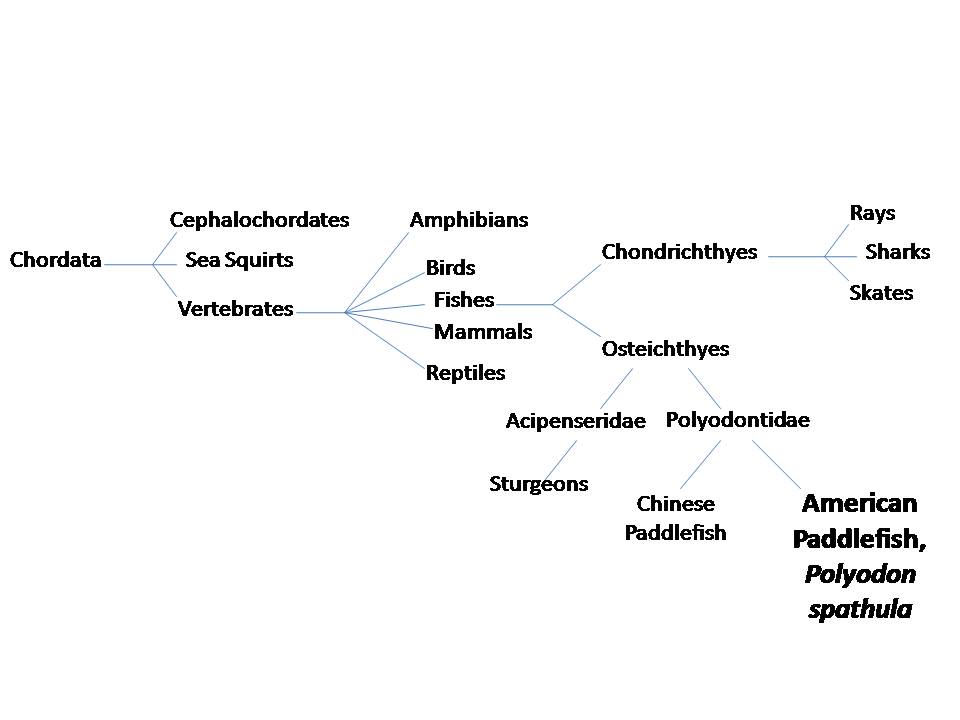
Phylogenetic Tree 1. This phylogenetic tree is constructed based on how the American Paddlefish fits into the Phylum Chordata which is based on morphological characteristics. This tree also shows the American Paddlefish's closest relatives: the Chinese Paddlefish and Sturgeons.
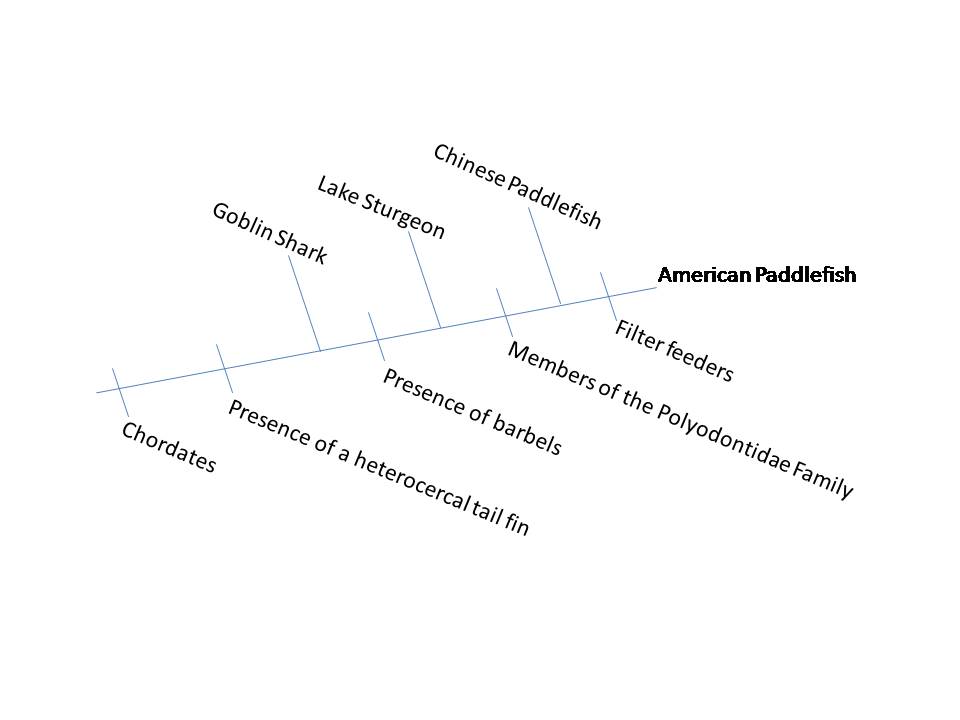
Phylogenetic Tree 2. This phylogenetic tree is a more detailed tree constructed based on specific morphological characteristics as well as the species' feeding habits. The species depicted in the tree are either directly related to the American Paddlefish or have similar morphological characteristics as the American Paddlefish. The Goblin shark is a shark that has a similar protruding rostrum like that of the American Paddlefish's rostrum.
To learn where the American Paddlefish lives, proceed to the Habitat page.
Visit
MultipleOrganisms.net to explore more organisms!
Visit the University of
Wisconsin-La Crosse, birthplace of the Multiple Organisms web pages!