Classification
Domain: Eukarya
All members of the domain Eukarya posses a true nucleus with
linear DNA as well as membrane bound organelles.
Kingdom: Plantae
The kingdom
Plantae are a group of eukaryotic organisms
that are generally photosynthetic, containing chloroplasts. They share a
freshwater algal
ancestor (green algae). There are many factors that
distinguish them from other kingdoms, but some of the main ones are the fact that
they posses
cell walls made of cellulose and they store their food as
starch.
Phylum: Magnoliophyta
This phylum consists of almost a quarter million
species of angiosperms, also know as
flowering plants. These plants, obviously,
posses seeds, however
their seeds have endosperms with in them. Additionally, they
posses flowers and fruits as well. Their
flowers, however, are not just for looks.
They
actually are specialized structures for sexual reproduction.
Class: Magnoliopsida
Magnoliopsida are also known as dicotyledons. Their
embryo consists of two cotyledons. Go to
Hibiscus rosa-sinensis or
Psidium guajava to compare
the common foxglove to other members of this class.
Order:
Scrophulariales
This consists of plants that usually have a superior
ovary and a lack of stipules. Additionally,
they either have an irregular corolla, fewer
stamens than
corolla lobes, or even both.
Family: Scrophulariaceae
The common name for the Scrophulariaceae family is
the figwort family. This family is characterized as having irregular
or bilateral flowers that are
bisexual. Also, another another very unique characteristic is
that their flowers have two pairs of anther-bearing stamens, as well
as a fifth stamen that is
sterile.
Genus: Digitalis
The common name of this genus is foxglove.
Their scientific name means finger-like, due
to the fact that the flower of a digitalis
can fit over a human
finger with ease.
Species: Purpurea
This species is classified as being biennial,
meaning that it takes two years for the
plant to complete its life cycle. This plant
is also the source of
Digitalis, which is prescribed by doctors for heart problems.
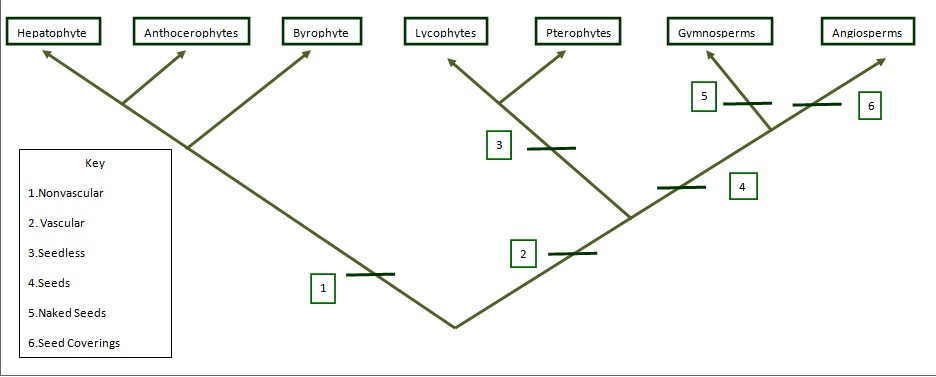
Here is a phlyogenetic tree of land plants. It shows how the Digitalis purpurea, which is an Angiosperm, relates to the rest of the land plants, ranging from Hepatophytes to Pterophytes. However, you might be wondering what Hepatophytes, Anthocerophytes, Byrophyte, Lycophytes, Pterophytes, Gymnosperms, and Angiosperms. Hepatophytes are liverworts. Antherocerophytes are hornworts. Byrophytes are mosses. Lycophytes include club mosses, spike mosses, and quillworts. Pterophytes include ferms, horsetails, and whisk ferns. Gymnosperms are are plants with naked seeds and Angiosperms are plants that use reproductive structures like flowers and fruits. This tree is based on the shared derived characteristics between these groups, as well as evolutionary interpretations.
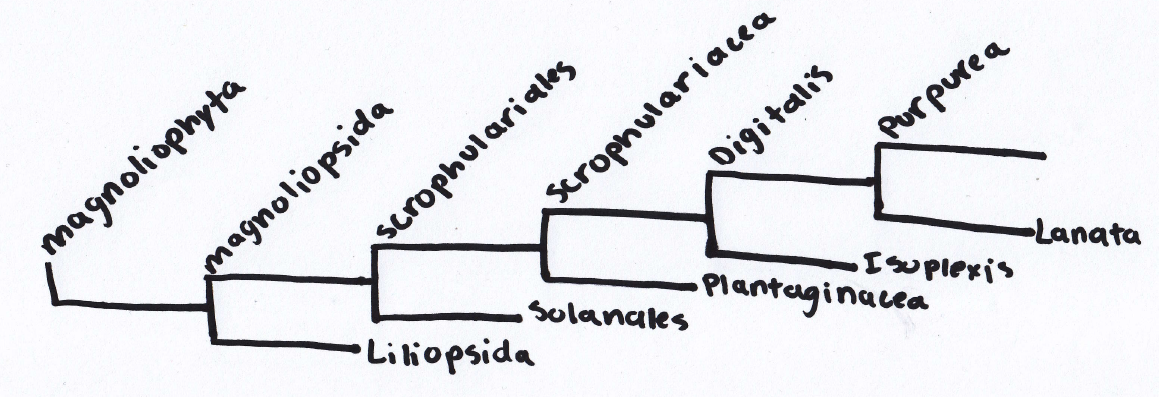
This tree shows the break down of the Digitalis pupurea starting from the phylum it is in, Magniolophyta. Then it breaks down into the class, order, family, genus, species, it is in (as shown on top). The classifications on the bottom are the closest related groups to each ranking.
To learn more about where you can find the common foxglove go to Habitats.