Habitat & Geography
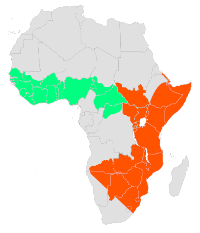 The Dendroaspis polylepis can be found
in parts of East and South Africa. Dendroaspis
polylepis prefer habitats such as savannahs,
open woodlands and rocky bluffs. The Black Mamba
takes shelter in termite grounds, hollowed trees,
mammal burrows and in some cases, the local homes of
unsuspected families. Black Mambas share their
habitat with lions, zebra, warthogs, wildebeest,
cheetah and elephants.
The Dendroaspis polylepis can be found
in parts of East and South Africa. Dendroaspis
polylepis prefer habitats such as savannahs,
open woodlands and rocky bluffs. The Black Mamba
takes shelter in termite grounds, hollowed trees,
mammal burrows and in some cases, the local homes of
unsuspected families. Black Mambas share their
habitat with lions, zebra, warthogs, wildebeest,
cheetah and elephants.
The Black Mamba is notorious for its diverse demeanor and is often described as a nervous snake. Dendroaspis polylepis typically hunt, eat, and sleep in the same area unless another animal forces it out. This species is predominately terrestrial. However, as its name implies ‘many scaled tree snake’ the Black Mamba is able to climb on trees in order to hunt prey or in some occasions to seek refuge. Black Mambas have adapted to their habitat by their slithering movement and ability to climb trees. Moreover, this species’ preference of arid environments has also contributed to its adaptation in its environment.
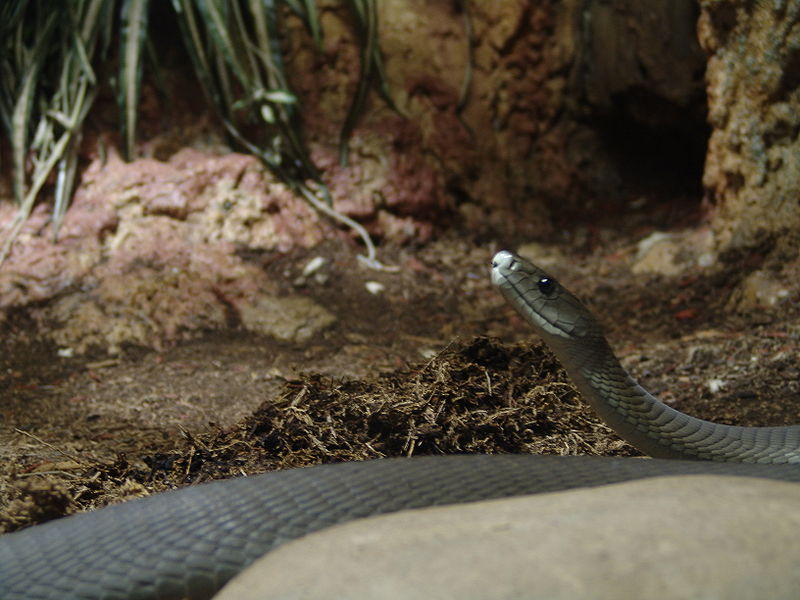 In its classification, Black Mambas are
classified into the Elapidae family. The
synapomorphy that unites this family is its venom.
Black Mambas kill their prey via venom or by
squeezing until it’s muscles give out and the animal
perishes. Black Mambas are labeled as predators and
prefer omnivorous animals. Their prey usually
consists of smaller animals such as birds, rodents,
frogs and occasionally other snakes.
In its classification, Black Mambas are
classified into the Elapidae family. The
synapomorphy that unites this family is its venom.
Black Mambas kill their prey via venom or by
squeezing until it’s muscles give out and the animal
perishes. Black Mambas are labeled as predators and
prefer omnivorous animals. Their prey usually
consists of smaller animals such as birds, rodents,
frogs and occasionally other snakes.
Click here to go to Home page