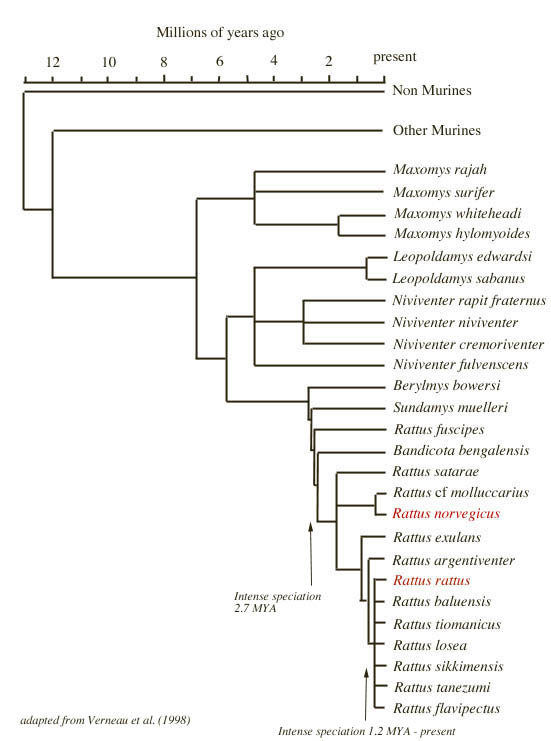
Classification
Domain: Eukarya
Kingdom: Animalia
Phylum: Chordata
Class: Mammalia
Order: Rodentia
Family: Muridae
Genus: Rattus
Species: R. norvegicus
Domain: Eukarya
·
All the organisms that have
cells containing true nuclei. This domain
includes many groups of single-celled organisms as
well as multicellular plants, fungi and animals. [2]
Kingdom: Animalia
·
Organisms are heterotrophs
meaning they eat other organisms or by eating non
living organic material. They are motile, lack
cell walls, and most reproduce sexually. [2]
Phylum: Chordata
·
They have bilateral symmetry
and considered to be deuterostomes. Chordates
have a notochord; a dorsal, hollow nerve cord;
pharynx geal slits or clefts; and a muscular,
post-anal tail at some point throughout development.
[2]
Class: Mammalia
·
Mammals have a mammary gland,
which produces milk for offspring. They
are endothermic, have prolonged parenting to teach
young survival skills, differentiated teeth, and
most have a high metabolic rate. [2]
Order: Rodentia
·
Rodents have continuously
growing incisors that need to be worn down by
gnawing. They are primarily herbivores and
generally small. [2]
Family: Muridae
·
Refers the Old World rats
that are now dispersed around the world; they are
distinguished from the Cricetidae due to the lack of
cheek pouches. [1]
Genus: Rattus
·
They can be described as a
common house rat that has bevel edged incisors. [1]
Species: R. norvegicus
·
It can be described as a common house hold rat that is known for being a pest. [1]

Copyright © 2004-2012 Free
Software Foundation, Inc. This work
is licensed under a Creative
Commons Attribution-No Derivative Works 3.0 license
(or later version)
Copy right @ 2003, 2004 All
rights reserved to Anne Hanson who earned a M.S. and
Ph. D in animal behavior
Previous to : Home Next to: Habitat