Equus burchelli (Plains Zebra) -BIO203
Classification
Domain: Eukarya
Kingdom: Animalia
Phylum: Chordata
Class: Mammalia
Order: Perissodactyla
Family: Equidae
Genus: Equus
Subgenus: Hippotigris
Species: Equus burchelli
Domain Eukarya: Zebras are in the domain Eukarya because they
are multi celled organisms with membrane organelles.
Kingdom Animalia: The zebra is in the kingdom Animalia because
they have no cell wall, have a gametic life cycle, and are
heterotrophic.
Phylum Chordata: The zebra is in the phyla chordata because they
have a postanal tail and a hollow nerve chord that lies dorsal
to the notochord.
Class Mammalia: Zebras are in the class mammalia because they
are endothermic, give birth to live young, have mammary glands,
and possess hair and fur for warmth.
Order Perissodactyla: Zebras are in the order perissodactyla
because they are toed-ungulates (animals with hooves).
Family Equidae: Zebras are in the family equidae because they
are medium to large animals. They are horse-like animals with
long heads and necks with a mane. Their ears can move and
they have dichromatic vision. Other members of the Equidae
family are donkeys and horses.
Genus Equus: Zebras are in the genus Equus because they live in
herds or bands. In Latin, Equus means horse or steed.
Equus burchelli: Equus means horse and burchelli means of the
plains of central and eastern Africa.
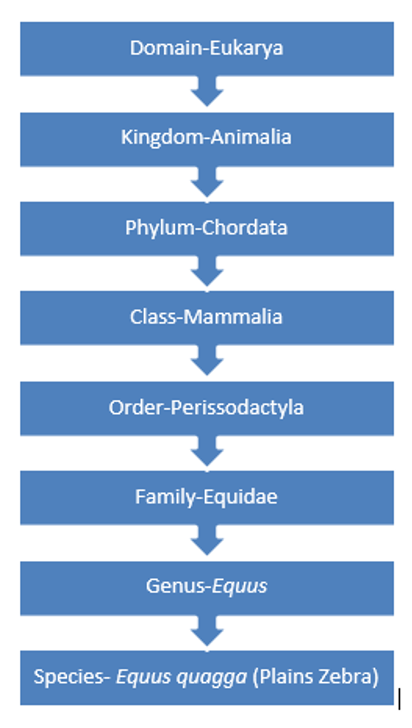
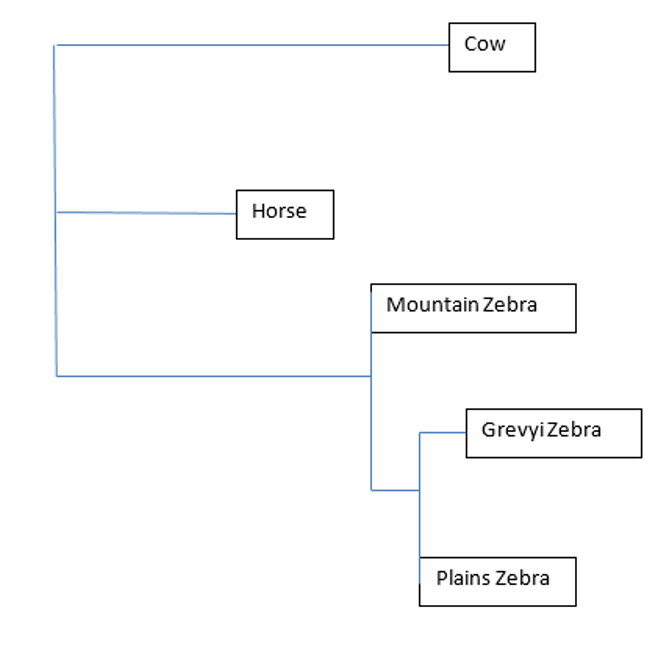
The above left diagram provides a visual representation for how the Plains Zebra is classified. The above right diagram shows the evolutionary relationship between the bovine, equine, and several zebra species.