
Classification
Domain: Eukarya
Kingdom: Animalia
Phylum: Chordata
Class: Mammalia
Order: Chiroptera
Family: Molossidae
Genus: Tadarida
Species: brasiliensis
Eukarya
The Tadarida brasiliensis is in the domain Eukarya because this species is multicellular with a nucleus and other organelles contained within a membrane. Members of the Eukarya domain also undergo cellular division by mitosis.
Animalia
The free-tailed bat is classified in this kingdom because they are heterorophs (relying on other individuals for energy) and multicellular individuals who do not have a cell wall but a cell membrane. They also belong to this kingdom because they ngest food and digest it in an internal cavity. (Myers, 2001)
Chordata
In the phylum Chordata, special features include a pharyngeal slit, dorsal nerve cord, notochord, and a post- anal tail. It is important to remember that these features need by present at some point in the organism's life in order for them to be classified as a chordate. A few other important features include bilateral symmetry, a complete digestive system, a closed circulatory system, and three germ layers. (Myers, 2001)
Mammalia
Organisms that fit into this class share three main characteristics not found in other classes. These characteristics include: three middle ear bones, hair, and production of milk by mammary glands (modified sweat glands). Mammalian organisms are mostly endothermic (warm-blooded) and rely on other sources of heat to keep warm. (Myers, 2001)
Chiroptera
The Tadarida brasiliensis fits into this order because it is the bat order. The bats of this order contain the modified forelimbs which support the wing membranes. Other characteristics include a short neck, slender and light-weight bones, and concentrated weight in the chest region. (Conway & Simmons, 1997)
Molossidae
Within the family Molossidae is where the Tadarida brasiliensis can be found next which contains the free-tailed bats. Bats are classified as free-tailed because their bony tail extends to the end of a developed tail membrane. Other features include short, strong legs, broad feet, and velvet-like fur. (Myers, 2001)
Tadarida
The organisms in this genus in order to be classifies as Tadarida, must reside in either Southern Europe and North Africa, parts of Asia and India and in the Southern United States, West Indies, and parts of South America.
Tadarida brasiliensis
This is the Mexican/Brazilian Free-Tailed bat! This bat is native to the Americans, has short velvet fur, and migrates south for the winter.
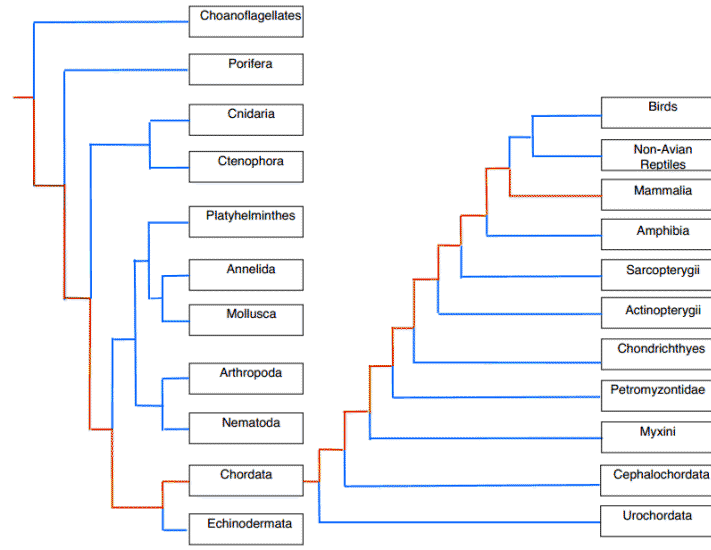
Figure 1. Phylogenetic tree showing the relationship of the phylum Chordata and class Mammalia created by Jesse Guadarrama.
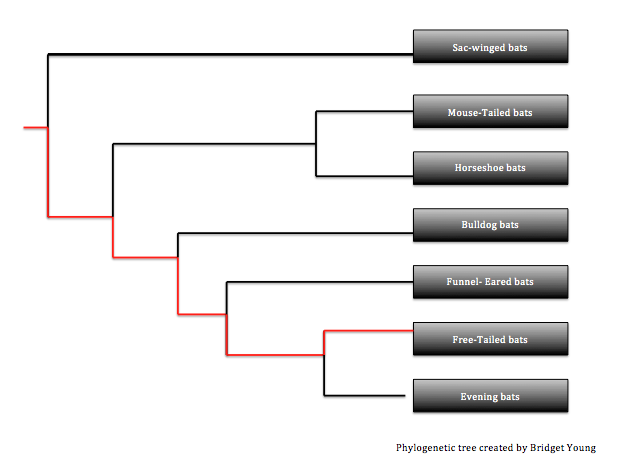
Figure 2. Phylogenetic tree showing the relationship of the order Chiroptera
Continue to habitat
Return to Home