|









| |
The Family Tree ...and the dreaded reunions 
|
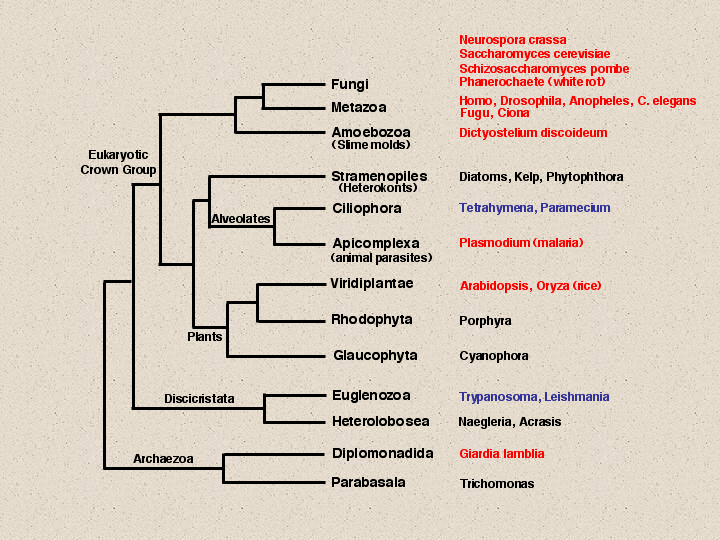
| Plasmodium falciparum is currently found in the kingdom Alveolata.
However, it used to be located in Protista. For many years, Protista was a "catch all" kingdom when the five kingdom system
was in
place. Since then, scientists have realized that many organisms differ
more greatly than what was originally thought, as a result the number of
kingdoms has grown.
|
Large Phylogenetic Tree:
|
|
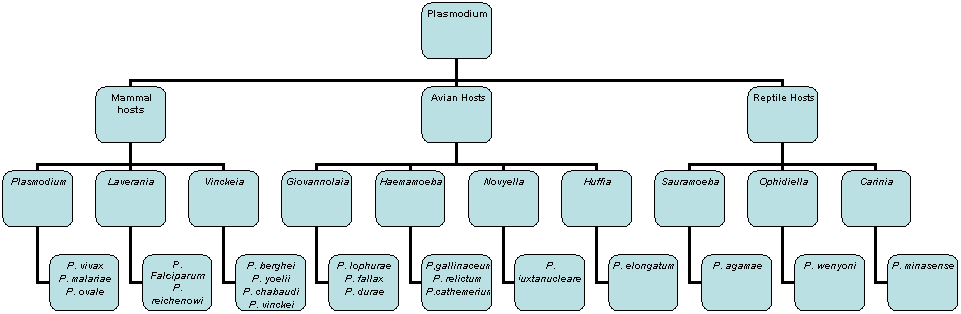
Small Phylogenetic Tree:
|
|
*Note: More species do occur in
some branches, however due to lack of space not all could be entered.
Made by Laura Augustine using information
from
Huestis
|
Classification:
Domain ~ Eukarya
Kingdom ~ Alveolata
Phylum ~ Apicomplexa
Class ~ Aconoidasida
Order ~ Haemosporida
Family ~Plasmodida
Genus ~ Plasmodium
Species ~ Plasmodium falciparum
Source: KEGG
|
Reasoning for Classification:
-
Domain - Plasmodium falciparum is considered
eukaryotic due to the cellular structure, and since it contains
organelles.
-
Kingdom - Alveolata contains protists that
used to belong to Protista, the artificial kingdom. While the
kingdom varies greatly, organisms in this kingdom do have
similarities in structure and genetics.
-
Phylum - Apicomplexa contains organisms that
have no individual form of motion, except for their gametes.
-
Class - Aconoidasida have a tip at the end of
their form which allows them to enter other organisms. They secrete
enzymes to aid in penetrating the other species.
-
Order -
Haemosporidia literally means blood
spores. All members of this phylum are parasitic in vertebrate
hosts.
-
Family - Plasmodium (Laverania) a family in Haemosporida.
Laverania was the old generic name for malaria causing Haemosporidia
protozoa (Center for Cancer Education).
-
Genus - Plasmodium
-
Species - Four forms of Malaria Plasmodium exist:
Plasmodium
falciparum, vivax, ovale, and malariae. Plasmodium falciparum
is by far the most deadly, which also leads to
increased research for a vaccine. It is the only
A huge help in identifying, classifying, and understanding this
complex organism was found when the genome for Plasmodium falciparum
was sequenced. To learn more about the sequencing of the genome
CLICK HERE.
|
|
Source of Small Phylogenetic tree:
Huestis |
| Descriptions of classification source: Dictionary.com |
|

