COUGAR
 "The
Phantom Cat""
"The
Phantom Cat""









"So, what's so
special about the cougar?"
Cougars have many adaptations that make them such successful organisms
in various aspects. They have 4-chambered hearts that have two different circuits which is
a characteristic that is also seen in humans (as well as other
felid species): a pulmonary circuit and a systemic
circuit. They are considered “warm-blooded” animals and have three
specialized vessels containing blood called veins, arteries, and capillaries.
Therefore, they have a closed circulatory system. The first benefit
of having an enclosed circulatory system is that there is enough pressure to

maintain a high flow rate throughout the body so all tissues receive the
required amount of oxygen that is needed. Having good blood flow is
essential, especially during exercise. Another benefit of having a closed
circulatory system is that blood can be shunted to specific vessels. This aids
in absorbing nutrients throughout the intestines after a cougar takes in a meal.
One feature that is special to the cougar is that it has a special mechanism for
warming its own blood. This mechanism is a net of blood vessels in a
cougar's neck and extremities and is called
rete
mirable or “miraculous net”.
Venous
blood going to the heart is warmed by nearby arterial blood that is flowing away
from the heart to ensure that the heart never receives cold blood that could be
a shock to it. Therefore, blood in the
upper extremities, lower extremities, and the brain is always colder than the
blood near the heart.
Cougars have
sometimes been previously coined “cold-hearted killers” when in fact they should
be really be called “cold-headed killers.”
 |
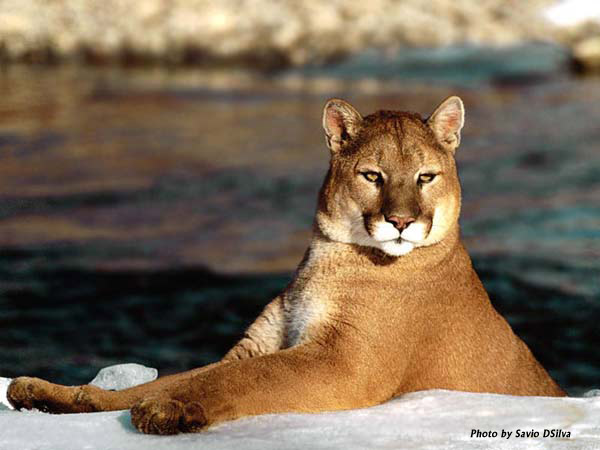
Cougars have thick fur that allows them to live in cold terrain because they do
not have much of a fatty layer under their skin. Their tawny-colored, grayish or
darkened fur coat allows them to blend in with their surroundings in mountainous
areas. In tropical areas cougars tend to be more of a reddish color due to its
brighter surroundings. Cougars spend long hours grooming their coat, and this
essential for keeping warm and minimizing their scent to other cougars and prey.
Cougars are very good swimmers which allows them to exploit new habitats
with relative ease. |
Cougars have strong, shortened jaws and elongated, sharp canine teeth
which allow them to capture and hold onto prey very tightly.
Cougar’s cheek teeth are also sharpened for shearing their food.
The skulls of cougars are drastically reinforced to withstand the
great pressure they are faced with when forcefully taking prey with
their mouths. They have very strong back legs for power and speed, but
flexible front legs for steering and maneuvering captured prey.
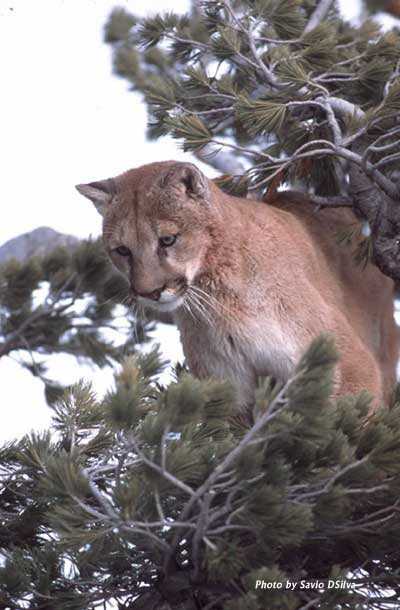
A cougar’s powerful hind legs also allow it to jump higher than
most other animals of its size, and this is why they are often spotted
in relatively tall trees. This amazing ability to jump to high spaces
allows them to escape predators if they feel they are in danger. Cougars
often sleep in trees for protection.
Their retractable claws aid in
climbing and capturing food.
|
 |
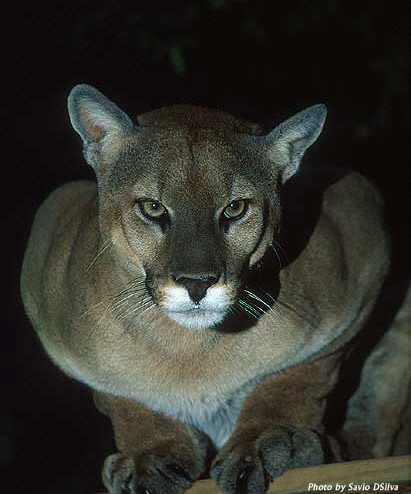 |
Like other cats, a cougar can crouch very low to hide in
relatively tight spaces.
Cougars hide so well that tracks in the mud or
snow are the only hints of their existence that most humans ever see.
Similar to other cats, a cougar’s
vision works best at detecting movement and allows them to see
relatively well in a dark environment- this is why cougars tend only to
move out in the open before dawn or at dusk.
|
Home
Classification
Habitat
Reproduction
Nutrition
Adaptations
Interesting facts
About me
References
Multipleorganisms.net
