Its Cool to Classify...
Domain:
Eukarya
![]() Has a distinct membrane-bound nucleus
Has a distinct membrane-bound nucleus
Kingdom: Plantae
![]() Eukaryotic, multicellular,
photosynthetic
Eukaryotic, multicellular,
photosynthetic
Phylum: Magnoliophyta
![]()
Class:
Magnoliopsida ![]() Eudicot-flower
parts are multiples of 4 or 5; root
system
Eudicot-flower
parts are multiples of 4 or 5; root
system
branching off from it; leaves have net-like veins;
vascular bundles are in a ring; 2 cotyledons.
Order: Rosales
![]() There
are no striking features that suggest
that the
There
are no striking features that suggest
that the
do share some similar wood characteristics and seed
anatomy; therefore, their grouping is dependent on
phylogenetic analyses of the DNA sequence data.
Family:
Rosaceae
![]() Diverse
group of economically valuable and
ornamental
Diverse
group of economically valuable and
ornamental
species; include trees, shrubs, and
herbs. Have five
a hypanthium which differs in shape depending on the
species and stage of development.
Genus:
Rosa
![]() Stems usually armed with thorns; leaves
are alternate
Stems usually armed with thorns; leaves
are alternate
toothed and their fleshy, berrylike “fruit” is known as the
rose hip.
Species:
Rosa multiflora![]() Multiflora
rose-perennial shrub that
forms dense,
Multiflora
rose-perennial shrub that
forms dense,
6-10 feet; leaves alternate, pinnately compound;
usually has thorns.
--The scientific name, Rosa multiflora, is translated to “multi-flowered rose” in English.
--Although the most common name for the specie is multiflora rose, there are multiple common names that Rosa multiflora is known by: baby rose, Japanese rose, seven-sisters rose, rambler rose, and the multiflowered rose. Some of these names are rather self-explanatory like the Multiflora Rose and the Multiflowered Rose. However, the name Japanese rose is representative of the country in which the species originated. While the remaining names (baby rose, seven-sisters rose, and rambler rose)all describe physical characteristics of the organism.
Phylogenetic Trees of Rosa multiflora
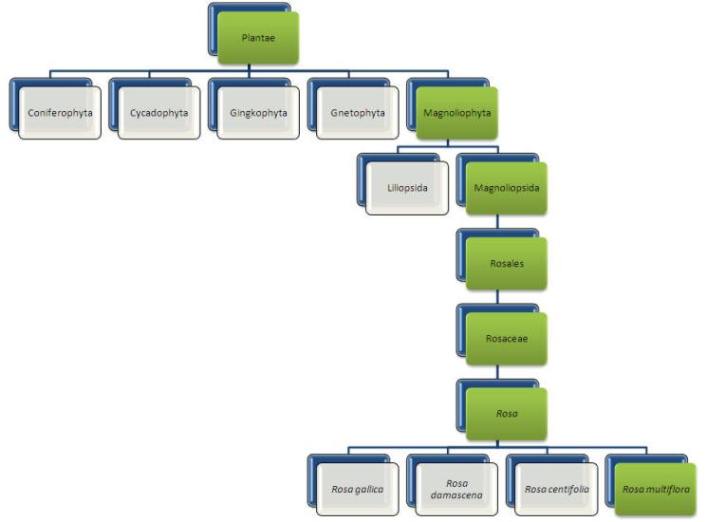
The tree above shows the relationships from the kingdom Plantae to the species Rosa multiflora. The phyla under Plantae are determined by the morphology of the species; however, as you move down the tree, the location of a species is no longer clearly determined by morphology, so DNA sequencing becomes involved in placing the species within a group. This is shown in the example below.
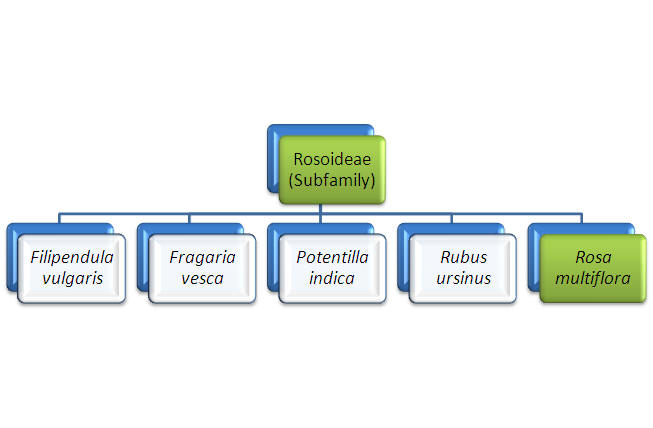
Within the subfamily Rosoideae, we will find Rosa multiflora. Filipendula vulgaris, Fragaria vesca, Potentilla indica, and Rubus ursinus are most closely related to the multiflora rose. Phylogenists determined the relationships between these species by examining their DNA sequences.
Copyright © 2007, Design by: Sunlight webdesign
