Cucumis sativus
Adaptation & Nutrition

A plants structure, and internal transport are both major adaptations made to help increase the ability of the plant to survive and thrive.
A plant's
structure, specifically angiosperms have
tissues(group of cells with common goal)
and organs(many tissues working for a
common goal). The three major
organs that contribute to its structure
are the roots, stem and leaves which
combined create the root system and the
shoot
system. The root system is
everything that lay beneath the soil and
the shoot system is everything above.
The root system contributes to the
plants ability to anchor itself to the
substrate, upta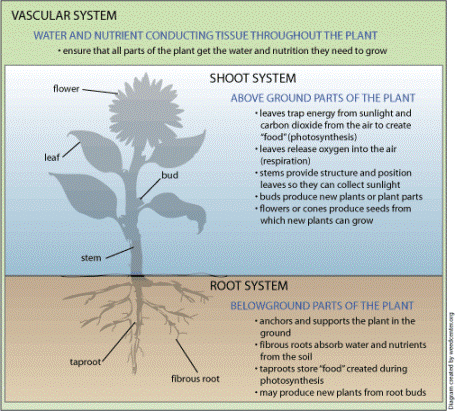 ke
nutrients(minerals and water) from the
soil and is used as a storage of sugars
and starches while the angiosperm is
either flowering or producing fruit. In
Eudicots like the cucumber, the root
system contains a taproot (as aposed to
a fibrous root) adapted to penetrate
deep into the soil to find ground water
not close to the surface. The
ability to uptake water is an important
function of the root system.
Uptake of minerals and water mostly
occurs at the tips of the roots where
small projections called 'root hairs'
are used to increase surface area.
These root hairs are constantly replaced
due to their short existence. Like the
modified stem/leaf the tendril, there
are also modified roots for example the
storage root which is seen in the
carrot.
ke
nutrients(minerals and water) from the
soil and is used as a storage of sugars
and starches while the angiosperm is
either flowering or producing fruit. In
Eudicots like the cucumber, the root
system contains a taproot (as aposed to
a fibrous root) adapted to penetrate
deep into the soil to find ground water
not close to the surface. The
ability to uptake water is an important
function of the root system.
Uptake of minerals and water mostly
occurs at the tips of the roots where
small projections called 'root hairs'
are used to increase surface area.
These root hairs are constantly replaced
due to their short existence. Like the
modified stem/leaf the tendril, there
are also modified roots for example the
storage root which is seen in the
carrot.
The stem's the organ of transport containing xylem and phloem which directs the flow of water to the leaves and sugars to the roots from the leaves (product of photosynthesis). The stem contains axillary buds, a terminal bud or apical bud and nodes and internodes. The axillary bud is a structure labeled above(bud) that has the ability to form a lateral shoot or branch with an apical bud at the tip and leaves. The apical bud, has the ability to stimulate growth, this is why pruning a shrub or tree(cutting of the apical bud) will make it bushier. The nodes are the point at which the leaves are attatched and the internodes are the segments of stem between them. Some type of stem modification is a tubers which is an enlarged end of a rhizome or stolon which is specialized in storing food, and create things like potatoes.
 Leaves
play an important role in plants. They
are the main site of photosynthesis
(conversion of light into energy in the
form of glucose). There are many
forms that a leaf can take including a
compound leaf, doubly compound leaf or a
simple leaf like the cucumber. The
simple leaf is named such due to its
undivided blade and is lobed edges.
In a Eudicot, the leaf viens are in a
net like fashion as apposed to the
parallel veination in monocots like
corn. A leaf modification that
is exhibited in the cucumber plant is a
tendril. This adaptation allows
the plant to climb up trellises or cages
for support and to gain better vantage
point(closer to the sun) for
photosynthesis.
Leaves
play an important role in plants. They
are the main site of photosynthesis
(conversion of light into energy in the
form of glucose). There are many
forms that a leaf can take including a
compound leaf, doubly compound leaf or a
simple leaf like the cucumber. The
simple leaf is named such due to its
undivided blade and is lobed edges.
In a Eudicot, the leaf viens are in a
net like fashion as apposed to the
parallel veination in monocots like
corn. A leaf modification that
is exhibited in the cucumber plant is a
tendril. This adaptation allows
the plant to climb up trellises or cages
for support and to gain better vantage
point(closer to the sun) for
photosynthesis.
Along with the plants structure, the ability of vascular tissues (transport tissues) xylem and phloem to move nutrients within the plant (similar to a humans circulatory system) is an adaptation enabling them to grow to to significant heights. Xylem, or the water-conduction system is composed of vessel elements (small tubes) and through the forces of adhesion (water adhering to a surface) and cohesion (water adhering to itself) is able to transport water from the roots to the leaves. Phloem, or the sugar-conduction system through sieve-tube elements which allow glucose made in the leaves to be transported to the roots.
Click
here to learn more about its life
cycle.
Copyright © 2007, Design by: Sunlight webdesign