BIO 203
Ah, the Tropical Climate
The purple form of the passion fruit grows in
subtropical regions, while the yellow passion fruit thrives in tropical
regions. Below is a map of the distribution for passion
fruit. Notice that it tends to be found in areas
with more sunlight. This
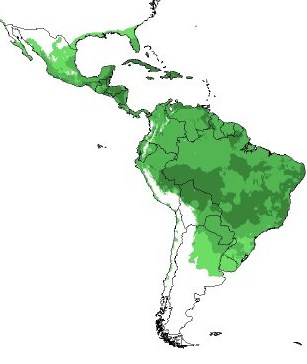 is due
to the fact that Passiflora edulis requires a lot of sun for
optimal growth and fruit production. In very hot places, partial shade
may be preferable.
is due
to the fact that Passiflora edulis requires a lot of sun for
optimal growth and fruit production. In very hot places, partial shade
may be preferable.
The vine that the passion fruit grows on can be a little out of control, so it is often planted next to a chain link fence or installed in a trellis (a structure used to support plants) before planting. The vines should be pruned often to ensure there is enough room for growth. In extremely hot areas, a canopy of foliage is usually left around the fruit to prevent sunburn. The vine and fruit also require a lot of water, especially when the fruits are maturing, so irrigation systems are often installed. If there is not enough water while P. edulis is maturing, the fruit will shrivel up and die. The passion fruit grows in soil that is rich in organic materials and low in salts, with an optimal pH around 6.5-7.5.
Adaptation
The purple passion fruit is subtropical and prefers a
frost-free climate. However, there are some locations that can take
temperatures into the upper 20's (°F) without serious damage. In fact,
the plant is grown in California as far north as San Jose. During cool
winters, vines may lose some of their leaves, but roots re-sprout even
if the main part of the plant is killed. Since the passion fruit is
acclimated to tropical/sub-tropical climates, it doesn't adapt well to
extreme changes. They do require maintenance and proper conditions for
ultimate growth.
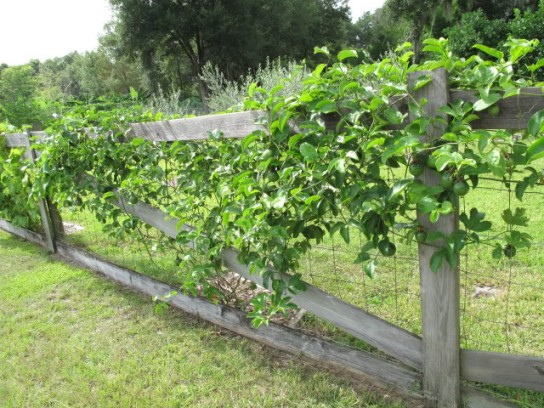

So we know that P. edulis lives in tropical areas. Now what kind of nutrition does it need? Let's find out by going to Nutrition.
Home