Classification Information
Domain: Bacteria
Kingdom: Bacteria
Phylum: Proteobacteria
Class: Gammaproteobacteria
Order: Enterobacteriales
Family: Enterobacteriaceae
Genus: Escherichia
Species: Escherichia coli O157:H7 (E. coli O157:H7)
Why that Classification?
Domain/Kingdom of Bacteria: E. Coli O157:H7 fits here because it is prokaryotic (meaning it has no nucleus, or membrane bound organelles), and unicellular.
Phylum of Proteobacteria: The major characteristic that
classifies E. coli O157:H7 is Gram negative meaning its outer
membrane contains mostly lipopolysaccharides.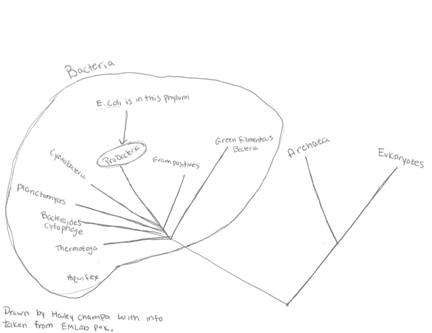
Class of Gammaproteobacteria: E. coli o157:H7 fits here because it is an anaerobic and fermentation gram negative bacteria.
Order of Enterobacteriales: E. coli O157 fits here because it is rod-shaped.
Family of Enterobacteriaceae: E. coli O157 is put into this category because it can be an animal parasite.
Genus of Escherichia: E. coli O157 is placed in this genus because it is mostly found in the human intestine but also present in soil and water.
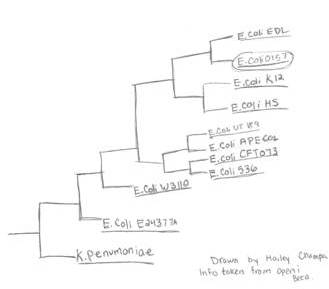
Species of Escherichia coli O157: This is one of the species that fall under the genus above. Throughout the site we will talk more about what makes this species unique. This strain was named this way because it is somatic giving it O it is the antigen 157 and finally it has a flagella giving it the H with antigen 7. you combine all of these and you get the strand O157:H7. You can see how distantly related the different strains of E. coli differ in the picture to the left.
Want to learn about more bacteria? Click on the following links to learn more!
Xanthomonas campestris
Streptococcus pyogenes
Bordetella pertussis
Clostridium difficile
Let us continue learning about E. coli O157 by learning about its Habitat.