Oleander (Nerium oleander)
Check Out These Cool Features!
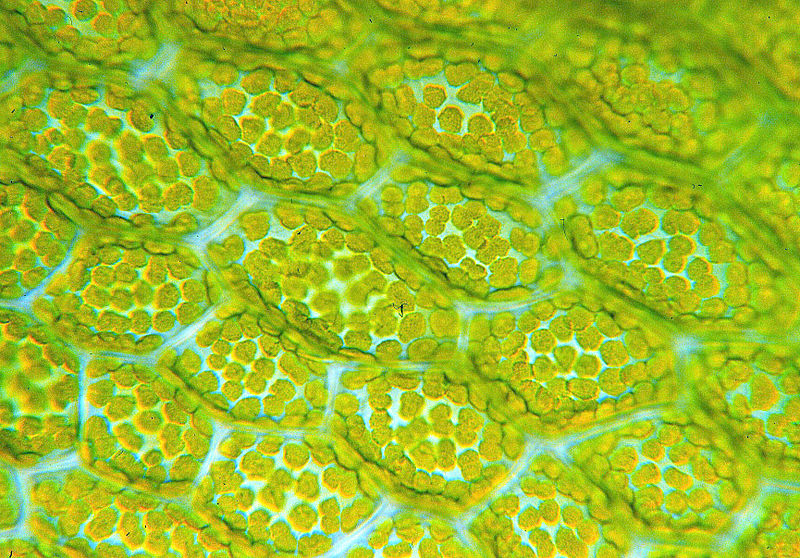
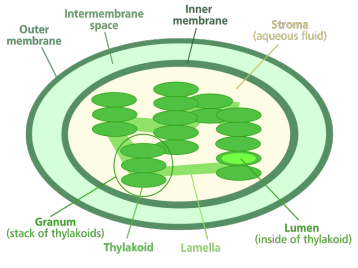
Chloroplasts:
Nerium oleander
has the capacity to
photosynthesize, which means that it has chloroplasts to
absorb the sun's energy. One could think of chloroplasts
as being very small solar panels that convert sunlight to
energy. Some other organisms that would have chloroplasts
would be
Milkweed,
Primrose, and
Horse Chestnut.
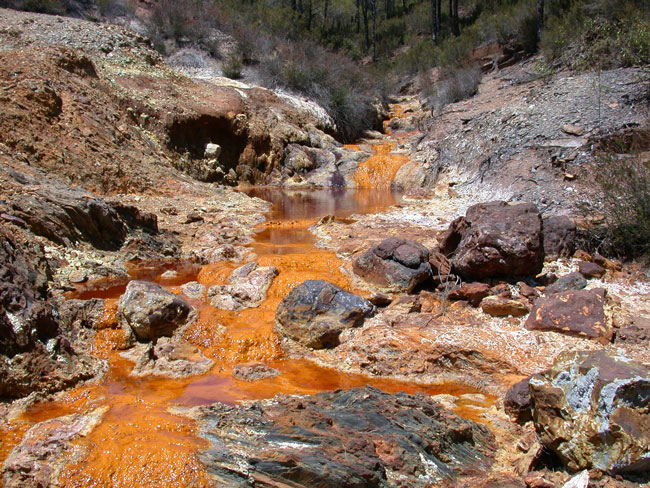
Phytoremediation:
Nerium oleander
can thrive in areas that have a very high amount of lead or
other toxic metals in their soil that normal plants would die
in. A study was done that looked at the different amounts of lead that
accumulated in the plant when it was grown in soil that had a
high lead content. What was interesting is that
most of the lead was kept out of the plant by the roots, but
what parts were absorbed for the most part stayed in the roots.
The lead did not go into the areal parts meaning that if this
plant were to be planted in an area with high lead
concentrations, there would not be toxic chemicals released into
the air. This excites many conservationists because this
plant could be planted in places, such as the Iberian Pyrite
Belt in Portugal, which have very high metallic sulfide
concentrations in their soils. This could enable phytoremediation to happen, phyto meaning plant and remediation
meaning to restore. If Nerium oleander was
planted in these areas, the toxic metal amounts would eventually
decrease and these places could once again be ecologicaly
thriving.


Drought Resistance:
Nerium oleander is considered to be very drought
resistant. This is because in times of less water it will
often slow its growth and stop flowering. It also has
mechanisms, such as a waxy cuticle on its leaves, to help prevent water loss.


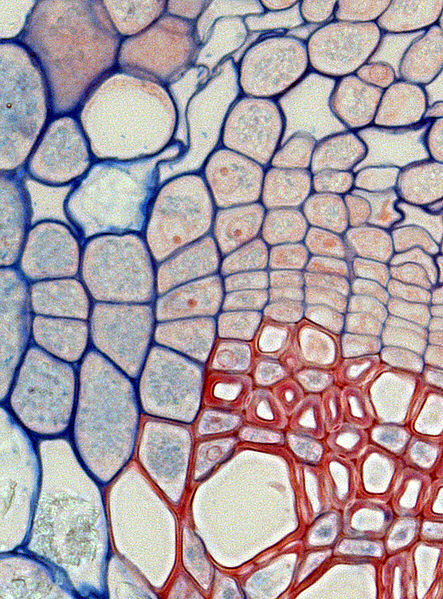
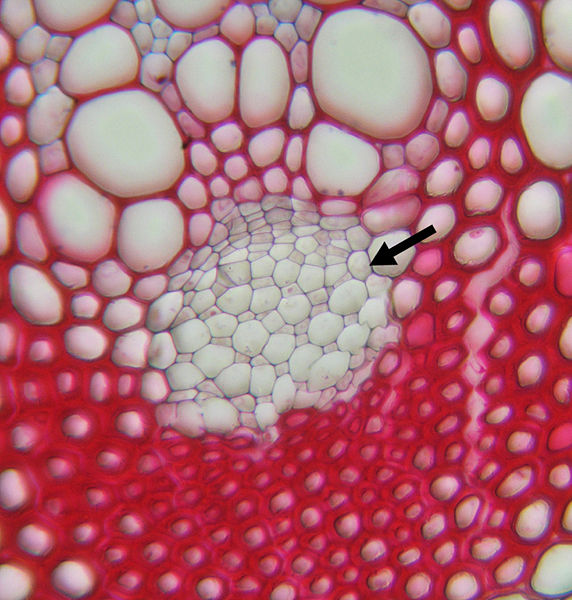
Vascular Tissue:
Nerium oleander contains xylem and
phloem, which aid in transportation in the plant. Xylem
primarily transports water and other nutrients from the soil and
phloem primarily transports sugars.
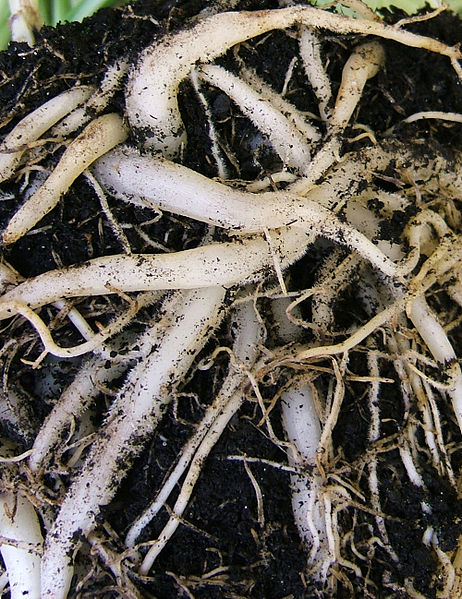
Roots:
Oleander has a root system which it uses for water and nutrient
uptake. The nutrients that are taken in are phosphorus,
potassium, nitrogen calcium, and other elements used for
different functions in the plant. For example: phosphorus is
used in making phospholipid-bilayers in cell membranes.


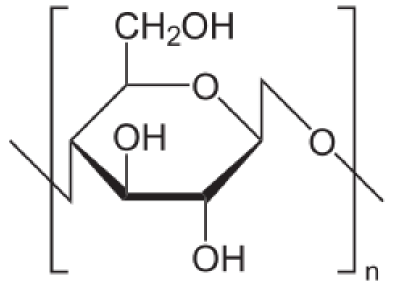
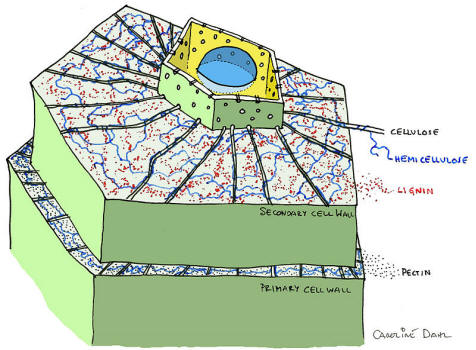
Cell Wall:
Oleander has cell walls made of cellulose. These
are really good at supporting this organism however the
consequence of that is that they limit its mobility.
Home
Nutrition









