Classification
The Texas Blind Salamander fits into these taxons.
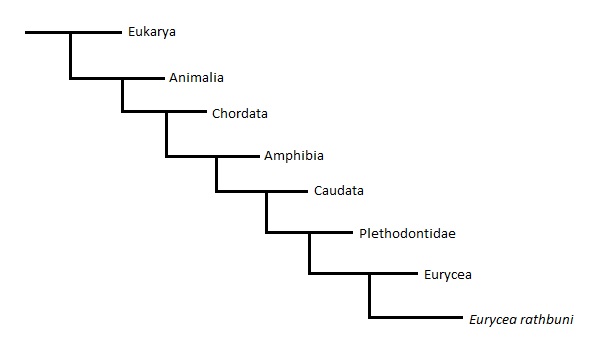
Figure 1. Phylogeny of the Texas Blind Salamander (Pyron 2011).
Domain - Eukarya
As a member of the domain Eukarya, this creature's cells contain a nucleus and membrane bound organelles such as mitochondria.
Kingdom - Animalia
The salamander fits into be kingdom Animalia because it is multicellular and has a fixed body plan, meaning it doesn't change shape or the location of its organs. It is also a heterotroph which means that it has to eat other organisms to gain its nutrients.
Phylum - Chordata
All members of the Chordata have, at some point in their lifecycle, a notochord, a hollow dorsal nerve cord, pharyngeal gill slits, and an endostyle and the Texas Blind Salamander is no exception.
Class - Amphibia
Members of the class Amphibia all aretetrapod vertebrates which are not amniotes, meaning they have a vertebrae and four legs but that need to lay their eggs in water otherwise the eggs will dry out and die.
Order - Caudata
Caudata is the order to which all salamanders and newts belong. They are lizard like in appearance but they don't have scales and they have to keep their skin wet.
Family - Plethodontidae
The family Plethodontidae is made up of salamanders that don't possess lungs, but instead respire through their skin, tissues around their mouths, or through gills like the Texas Blind Salamander.
Genus - Eurycea
Eurycea is a genus of salamanders commonly known as brook salamanders.
Species - rathbuni
This is the species name of the Texas Blind Salamander.
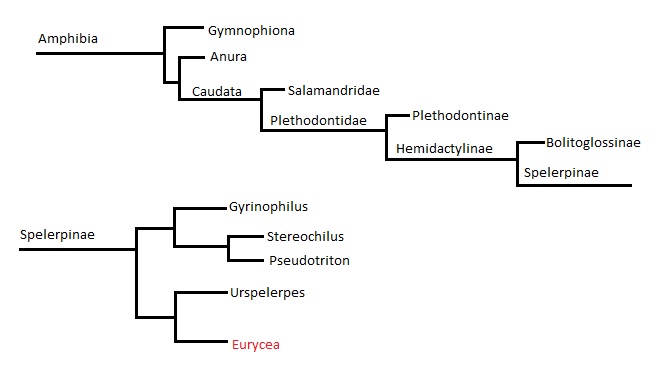
Figure 2. Phylogenetic tree showing the orders,
families, sub-families, and genuses to which the Texas Blind salamander
is related (Pyron 2011).
The Texas Blind Salamander is most
closely related other salamanders of the genus Eurycea but outside of
this genus, it is most closely related to the salamanders of the Urspelerpes genus.
Lets swim over to the Habitat page to see where this critter lives.

