Facts
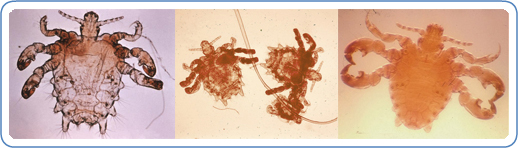
Clinically, infestations of Phthirus pubis are classified as pediculosis. Such infestations lead to burning, itching, secondary infections from scratching, as well as scarred, hardened, and often unnatural pigmentation of the skin in the infected area. Crab louse infestations can be diagnosed by microscopically inspecting the hairs of the possibly infected region for the lice or the eggs. One should be careful to differentiate between an active infestation (live adults or nymphs) and an inactive infestation (empty egg cases). Live eggs contain the embryo of the developing insect, while empty eggs lack a distinctive porous cap on the outer shell. Phthirus pubis strictly parasitizes humans, while head and body louse are known to adapt to life on other animals, such as pigs and dogs (Horsfall 1962). Those infected with Phthirus pubis should also be screened for other sexually transmitted diseases.
For more information on pubic lice treatment, please see the CDC website.
Go Home