Reproduction
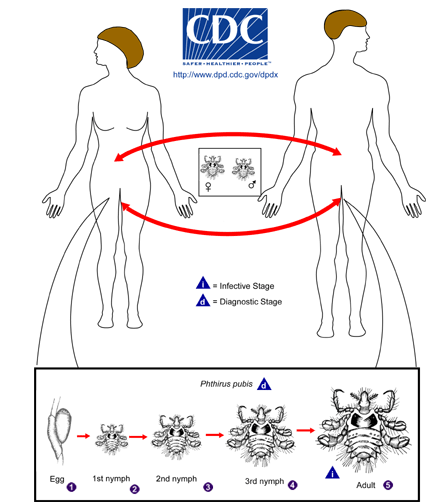 Humans serve as the host for
Phthirus pubis, which is mainly
transmitted by sexual contact. Phthirus pubis is found in
coarse hairs, most commonly in pubic hair, but infestation
frequently extends to hair around the anus as well as hair on
the abdomen and thighs. It may also be found occasionally
on the eyelashes of children. Phthirus pubis dispersal is
linked to hair density. Crab louse is most commonly found
it the pubic hair because the spacing between the hairs matches
the hind leg span of the crab louse. The four hind legs
are used for locomotion by attaching to two hairs. Crab
lice are dioecious, meaning there are two separate male and
female lice, and reproduce sexually. One to two days after
mating the female begins laying three eggs a day. On
average, the female will lay 26 eggs total. Once the eggs
are laid, they attach to the base of a single hair.
Phthirus pubis eggs appear dark opaque brown with a hard chitin
covering. There is a seven to eight day incubation period
after which the larva emerges. Over the next thirteen to
seventeen days, the larva sheds its skin three times before
becoming an adult. The adult crab louse has a lifespan of
about a month. The adult crab louse also appears dark grey
to brown in color and moves a relatively small amount
(Fisher and Morton 1970).
Humans serve as the host for
Phthirus pubis, which is mainly
transmitted by sexual contact. Phthirus pubis is found in
coarse hairs, most commonly in pubic hair, but infestation
frequently extends to hair around the anus as well as hair on
the abdomen and thighs. It may also be found occasionally
on the eyelashes of children. Phthirus pubis dispersal is
linked to hair density. Crab louse is most commonly found
it the pubic hair because the spacing between the hairs matches
the hind leg span of the crab louse. The four hind legs
are used for locomotion by attaching to two hairs. Crab
lice are dioecious, meaning there are two separate male and
female lice, and reproduce sexually. One to two days after
mating the female begins laying three eggs a day. On
average, the female will lay 26 eggs total. Once the eggs
are laid, they attach to the base of a single hair.
Phthirus pubis eggs appear dark opaque brown with a hard chitin
covering. There is a seven to eight day incubation period
after which the larva emerges. Over the next thirteen to
seventeen days, the larva sheds its skin three times before
becoming an adult. The adult crab louse has a lifespan of
about a month. The adult crab louse also appears dark grey
to brown in color and moves a relatively small amount
(Fisher and Morton 1970).
Learn about Interactions next!
Go Home