Habitat
 Metaleptea brevicornis
are found in the northeastern
United States, southeastern United States, and also Texas
(Donato and Cigliano
2000). In
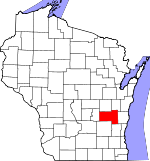
Wisconsin, this species has been reported in Fon du Lac County
(Kirk and Bomar 2005). Metaleptea brevicornis
are found in the northeastern
United States, southeastern United States, and also Texas
(Donato and Cigliano
2000). In
Wisconsin, this species has been reported in Fon du Lac County
(Kirk and Bomar 2005). |
 |
Nymphs and adults are typically found in areas on sedges and grasses near water and near seacoasts. Grasshopper population seems to be at its highest when precipitation is low. In other words, they like dry weather! The exact reason is unknown but it is believed that increased precipitation may cause drowning and an increase in fungal pathogens (Burst et al. 2007). |
Who lives with the Grasshoppers?
 Grasshoppers in the order Orthoptera
prefer grassland habitats. Grasshoppers can be found all throughout the world
and the other organisms that share the grasslands can vary. Examples of other
organisms that live with grasshoppers include: deer, rabbits, snakes, the
Monarch Butterfly, crickets, ants, lady beetles, dragonflies, damselflies, and
many other beetles (Hamilton Naturalists' Club Last update
unknown).
Grasshoppers in the order Orthoptera
prefer grassland habitats. Grasshoppers can be found all throughout the world
and the other organisms that share the grasslands can vary. Examples of other
organisms that live with grasshoppers include: deer, rabbits, snakes, the
Monarch Butterfly, crickets, ants, lady beetles, dragonflies, damselflies, and
many other beetles (Hamilton Naturalists' Club Last update
unknown).
Grasshoppers help recycle?!?
Grasshoppers (Orthoptera) have a major impact on plants because they change the
way nitrogen cycles in their grassland habitat. They speed up the process of
nitrogen recycling by eating plants that take longer to decompose. This in turn
allows plant production to increase. Grasshoppers also benefit the plants with
their feces (called frass) which give them nutrients. When grasshoppers die,
their body decomposes and gives the soil mineral and vitamins
(Gilroy 2011).
Agricultural Massacre!!
Grasshoppers do, however, have a negative effect on plants and crops. When
grasshopper population is high, they create a lot of agricultural damage to
alfalfa, soybeans, corn, cotton, clover, and tobacco. With the help of predators
like birds, snakes, frogs, and even humans, they help control the grasshopper
population (Glogoza and Weiss 1997).