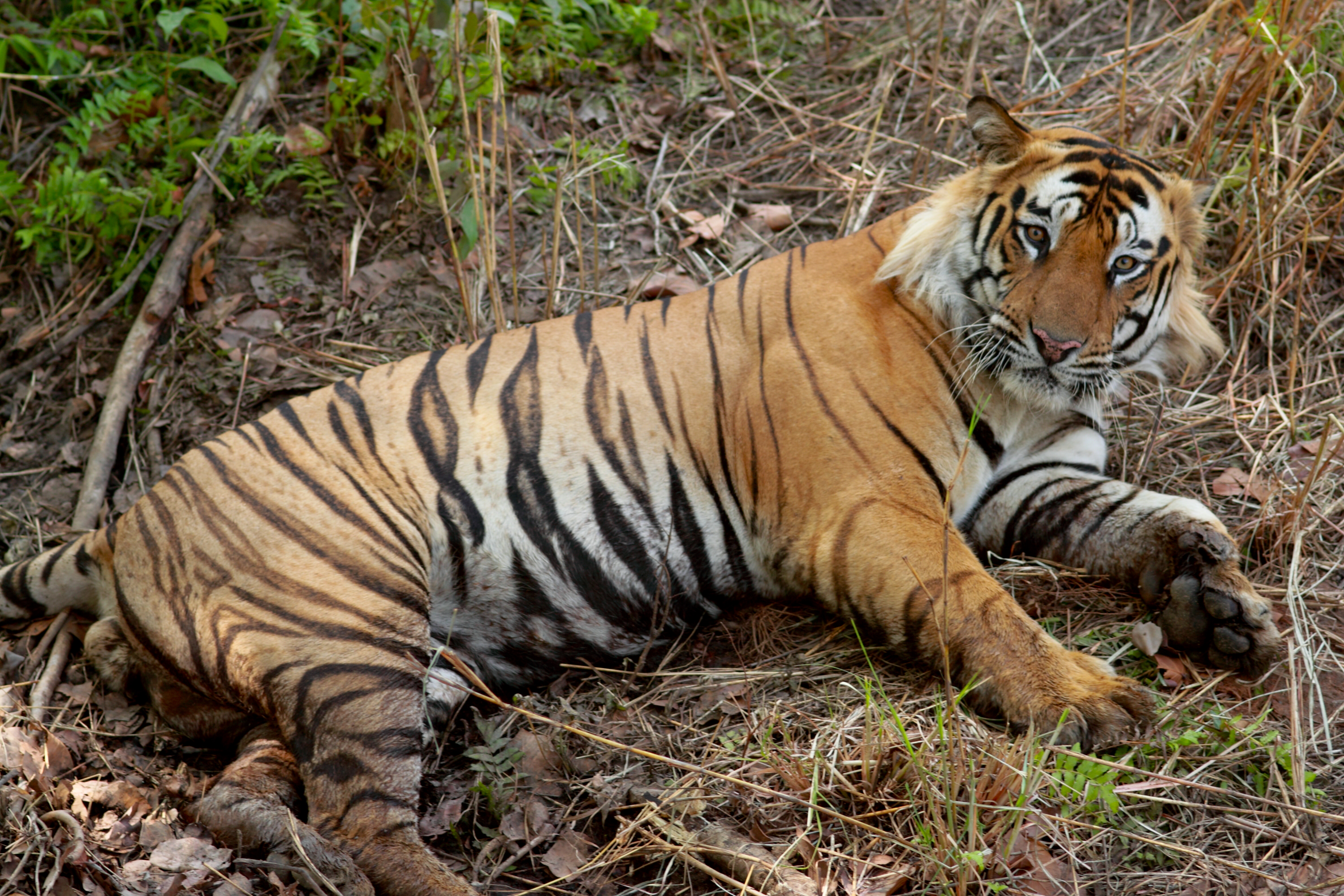
Classification
Domain: Eukarya
Kingdom: Animalia
Class: Mammalia
Order: Carnivora
Family: Felidae
Genus: Panthera
Species: Panthera tigris
Below are descriptions to each taxonomic group and why Panthera tigris belong in each group
Domain:
Eukarya All members within this domain have a true nucleus within a nuclear envelope and membrane bound organelles. The tiger’s cells satisfy these characteristics.
Kingdom: Animalia
Tigers belong in this group because all members are multicellular and are heterotrophs that depend directly or indirectly on other organisms for nourishment.
Phylum: Chordata
Tigers along with other chordates have a notochord, three germ layers, a hallow nerve cord and a tail projecting beyond the anus at some point of development.
Class: Mammalia
All members in the class mammalia including tigers produce milk for their young, have three middle ear bones and have hair on the skin.
Order: Carnivora
Tigers belong in this group because they rely heavily on animal tissue or meat for nutrition and energy.
Family: Felidae Tigers belong in this taxonomic category because all members are specialized hunters that rely mainly on prey they have killed themselves
Genus: Panthera This genus includes four species of animals the tiger, lion, jaguar and leopard. One unique characteristic of the species in this genus is the ability to roar. (Encyclopedia of Life 2013).
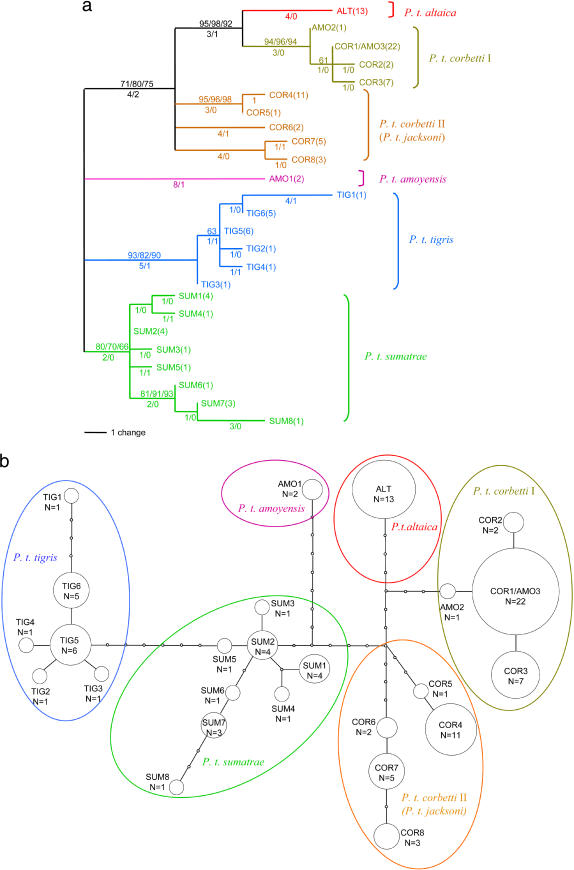
The picture above is a phylogenic tree depicting the differences in different tiger like species based on DNA evidence. Panthera tigris is in blue font.
Read more about the Habitat of the Panthera tigris
Back to Homepage