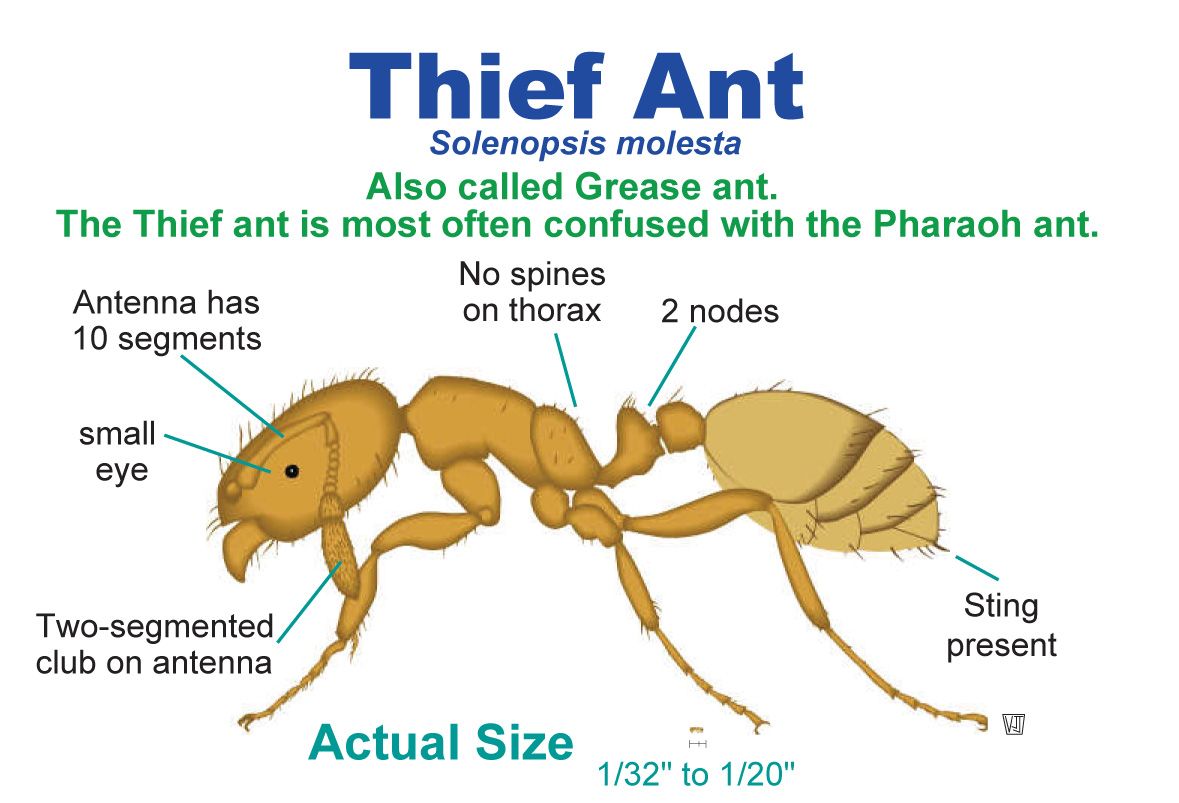
Form and Function
Thief ants are exceptionally small compared to the average
ant. They can be as small as 0.5 mm (Texas
A&M University, 2010).The workers eyes are minor, flat
and oval and the mandibles of the workers are four-toothed (Hayes,
1920). Compared to the worker ants of
Solenopsis molesta, the queens are much larger in size.
Queen thief ants can grow up to 5 mm long (Texas
A&M University, 2010). The queen and male ants
develop wings that are composed of hyaline. For the queens once,
it has mated the two pairs of wings fall off (McColloch
and Hayes,
1916). When observing a thief ant, one will
see a stinger at the end of the abdomen and a 10 segmented
antenna on its head. On the Antennae there is a 2 part segmented
club. (University of Nebraska, 2013)
Another distinguishing feature of the thief ant is its golden
yellow body color (Texas A&M
University, 2010). They use their small size to their
advantage by invading packaged food and stealing its contents. (Texas
A&M University, 2010).
Along with differences in structure, workers, males, and
queens also differ in the role that they plan in the community (Hayes,
1920). Worker ants are classified as a female that is
undeveloped. Workers live by their name and are the ones that have
the most jobs. These jobs include caring for eggs, and constructing
the nest (Hayes, 1920).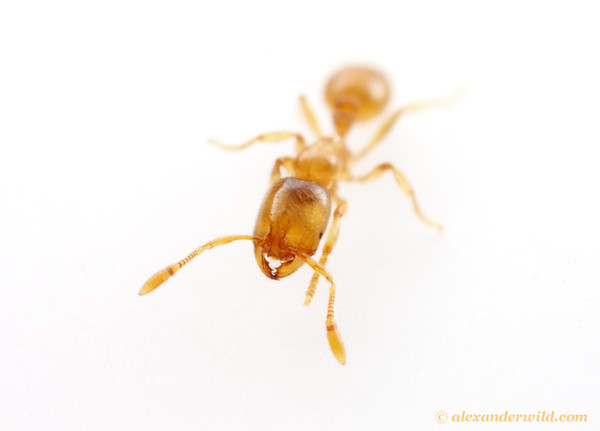 They are
responsible for caring for the young up until they become mature.
The main responsibilities for the queen, on the other hand, are to
reproduce and choose where the colony is going to live (Hayes,1920).
Males in the species Solenopsis molesta are larger in size
than the workers, and darker in color than the females. They only
function that the males serve as in the colony are to mate (Hayes,
1920).
They are
responsible for caring for the young up until they become mature.
The main responsibilities for the queen, on the other hand, are to
reproduce and choose where the colony is going to live (Hayes,1920).
Males in the species Solenopsis molesta are larger in size
than the workers, and darker in color than the females. They only
function that the males serve as in the colony are to mate (Hayes,
1920).
In regards to habitat thief ants have adapted to living in
many different types of environments, besides ones that are directly
in the sunlight (Hayes, 1920). Out of
all their senses, thief ants rely the most on their sense of smell
due to their poor hearing and vision (Hayes,
1920).