Classification
Domain: Eukarya
This species is a part of the domain Eukarya because it has a
true nucleus and has membrane bound organelles. Another
eukaryotic organism is the Danaus plexippus, also known
as the Monarch Butterfly (Encyclopedia of Life 2013). For more information on the Monarch
Butterfly click
here.
Kingdom: Animalia
This species is a part of the kingdom Animalia because it is
heterotrophic, meaning it relies on plants and other species to
gain energy. In contrast to plants, animal cells do not have a
rigid cell wall made of cellulose. (Encyclopedia of Life
2013). This kingdom has a vast diversity of organisms, including
Ursus maritimus, commonly known as the Polar Bear. Click
here to learn more about this organism.
Phylum: Arthropoda
This species is a part of the phylum Arthropoda because it has
the unique characteristic of ecdysis, meaning that it molts. In
order to grow, arthropods must shed their exoskeleton as these
cannot develop with the organism. In addition, the Eastern Carpenter
Bee is equipped with jointed limbs. These limbs allow
for greater mobility and movement. Another characteristic that
groups Xylocopa virginica into the Arthropoda phyla would be that it
has bilateral symmetry. This means that this organism has
identical structures on both the right and left side of their
body. Arthropoda is a vastly diverse phylum that makes up around 80% of the
kingdom Animalia. (Encyclopedia of Life 2013).
Class: Insecta
This species is a part of the class Insecta which makes up about
two thirds of the phyla Arthropoda. X.virginica has
three body sections including a head, thorax, and abdomen.
Insects are the only invertebrate to accomplish flight by
utilizing either one or two pairs of wings. When not in flight,
the class Insecta accomplishes movement on the ground by using
three pairs of legs (Encyclopedia of Life 2013). Click
here to see the Common Green Darner Dragonfly, Anax junius,
an organism that embodies these characteristics.
Order: Hymenoptera
Hymenoptera can be broken into two words, "hymen-" meaning
membrane and "-ptera" meaning wings (Meyer 2009). This species
is a part of the order Hymenoptera which encompasses wasps, bees,
ants, bumblebees, sawflies, and parasitic wasps. All of these
organisms
have two pairs of wings that have fewer veins compared to other
insects (Encyclopedia of Life 2013). The two sets of wings are
linked together and form a single surface to create more
effortless flight (Meyer 2009).
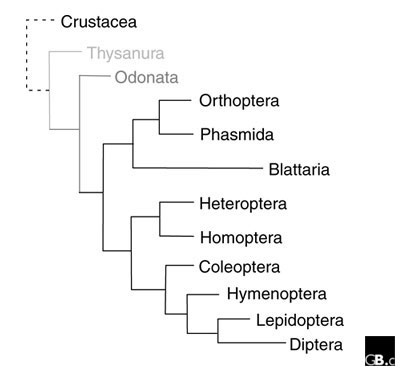
Figure 1. X. virginica is a part of the order
Hymenoptera. This order is closely related to the orders
Lepidoptera and Diptera. The order Lepidoptera is made up of
butterflies and moths, while order Diptera consists of flies
(BugGuide 2013). This data is displayed morphologically showing
the names of each order and their relatedness to other orders.
Family: Apidae
All members of the family Apidae are bees. This
family is made up of Honey Bees, Digger Bees, Cuckoo Bees, and
Bumblebees. The bodies of these bees contain more hair than
other Hymenoptera including wasps and ants (BugGuide 2013).
Genus: Xylocopa
Xylocopa is latin for "woodcutter" (Encyclopedia
of Life 2013). Xylocopa refers to large Carpenter Bees
estimated to be around 20 mm or larger (Grissell et al. 2011). Their abdomens differ
greatly from honey bees as they have smooth black abdomens
compared to a hairy abdomen on the honey bee. Xylocopa males can
be distinguished as having much larger eyes than females. These
bees choose wood as their preferred habitat (Encyclopedia of
Life 2013). To learn more about X. virginica nesting
strategies visit our
Habitat page.
Species: Xylocopa virginica
Xylocopa virginica is commonly known as the
Eastern
Carpenter Bee.This organism contains characteristics
that have researchers debating whether it is eusocial or
solitary (Richards 2011).
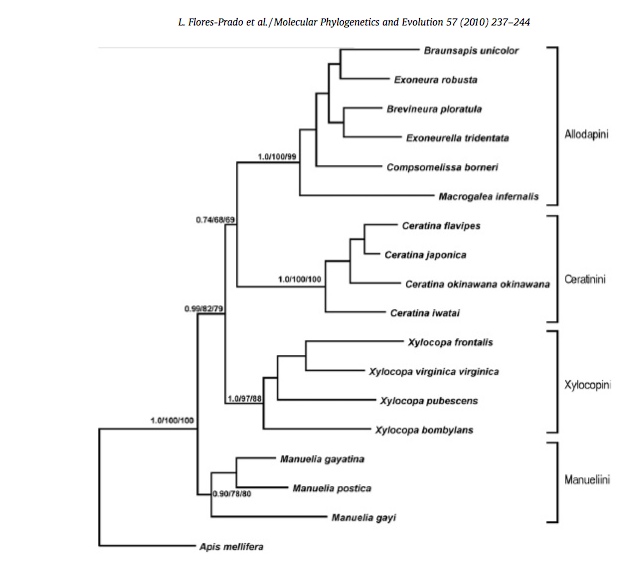
Figure 2.
This phylogenetic tree shows the relationships that
X. virginica share with other bees. From this tree it can be seen that
X. virginica forms a sister group with Xylocopa
frontalis. X. virginica is part of the clade
Xylocopinae. This clade also consists of Xylocopa frontalis,
Xylocopa pubescens, and Xylocopa bombylans. This
data is displayed morphologically (Flores-Prado et al.
2010).
Continue to
Habitat
Return to
Home
Go to
References