|
Current Level |
||||||||||||
|
|
||||||||||||
|
Previous Level |
||||||||||||
|
|
||||||||||||
|
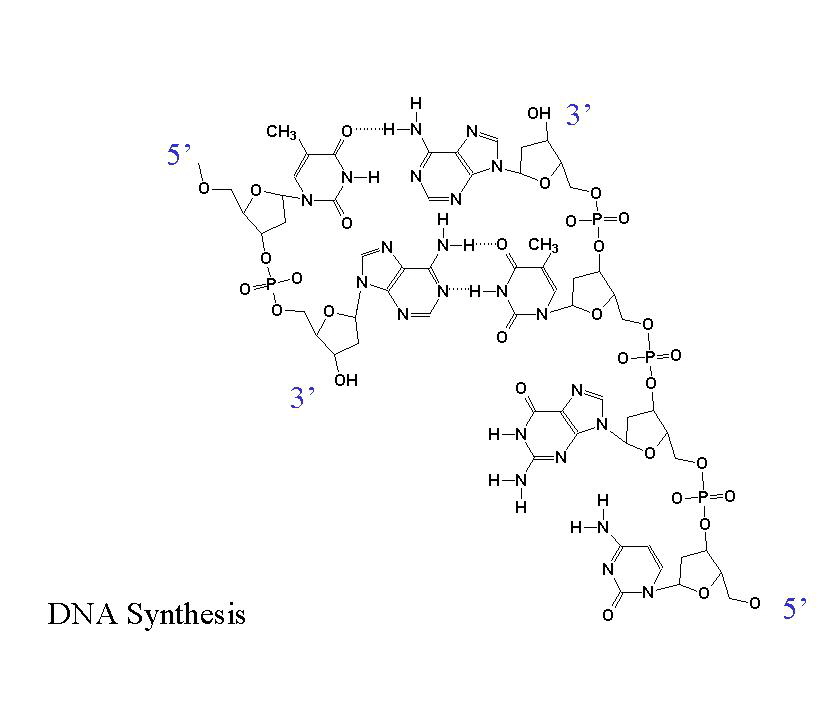
When DNA is synthesized the free 3´ hydroxyl (OH) group from the growing strand of DNA attacks the a phosphate on the next base to be added (see the red arrows below). Pyrophosphate is released and the new base forms a phosphodiester bond with the growing strand of DNA. The free 3´ hydroxyl group is then free to attack the next base to be added. This reaction is catalyzed by DNA polymerases. Similar reactions are catalyzed by RNA polymerases in the synthesis of RNA.
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|